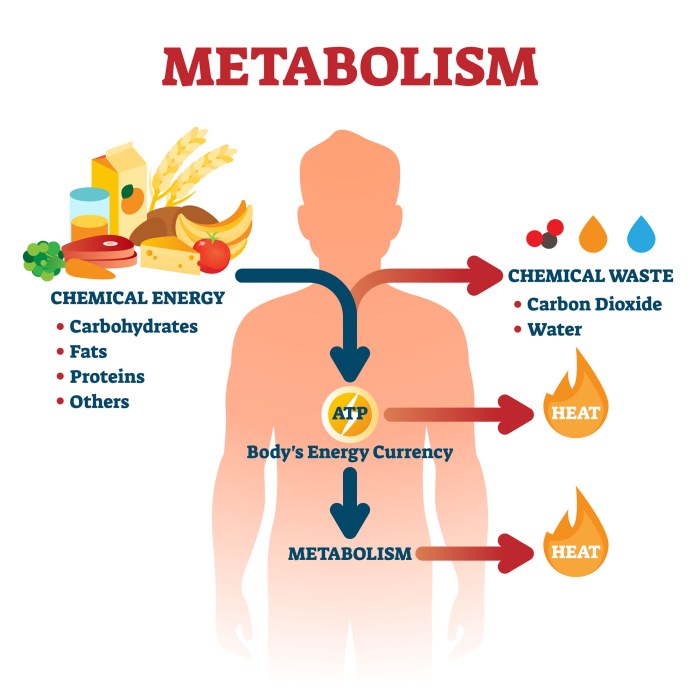
As we gracefully step into our fourth decade of life, our bodies undergo a series of fascinating transformations. Metabolism changes over 40, affecting our energy levels, weight management, and overall well-being. Join us on an interactive journey as we explore these shifts and empower you with knowledge and strategies to navigate this exciting phase with vitality and confidence.
From hormonal fluctuations to lifestyle adjustments, we’ll delve into the science behind metabolism changes and provide practical tips to optimize your metabolic health. Get ready to unlock the secrets of your body and embrace a new chapter of vibrant living.
Physiological Changes
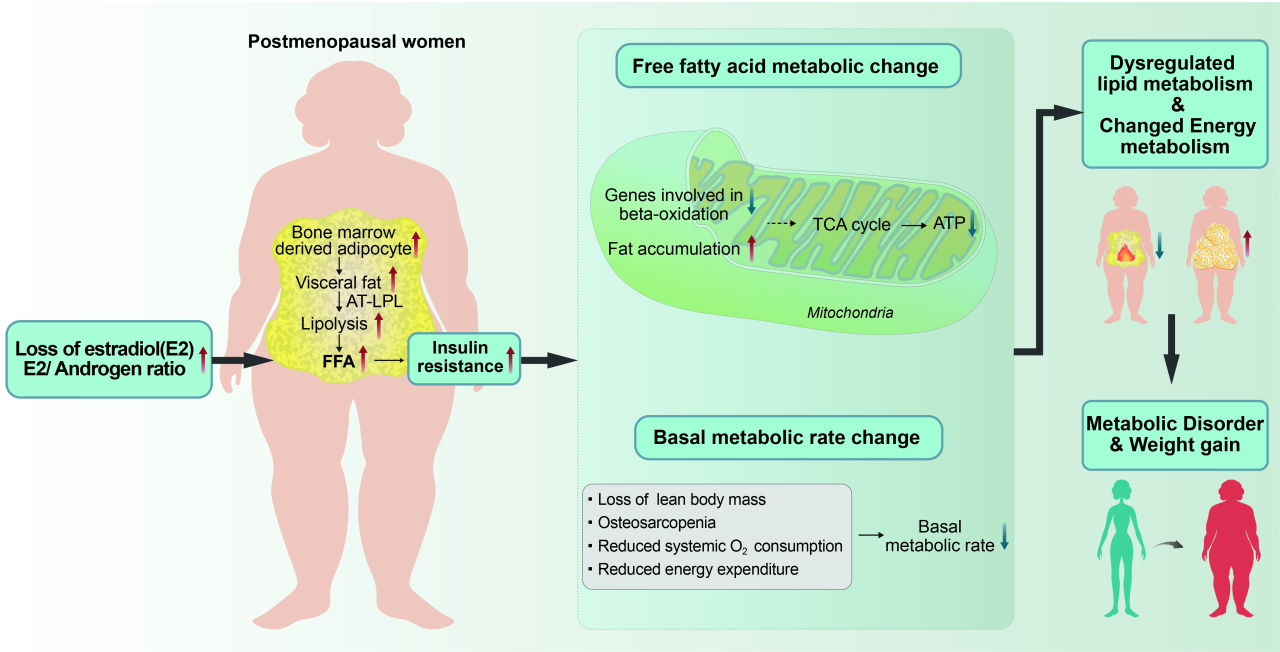
As we step into the fourth decade of life, our bodies undergo a series of physiological changes that can impact our metabolism. These changes are primarily driven by hormonal shifts, alterations in body composition, and a decline in basal metabolic rate.
Hormonal Changes
During this decade, the production of sex hormones, such as estrogen and testosterone, begins to decline. This hormonal shift can affect metabolism in several ways. For instance, declining estrogen levels can lead to a decrease in muscle mass, which can further contribute to a reduction in basal metabolic rate.
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) and Energy Expenditure
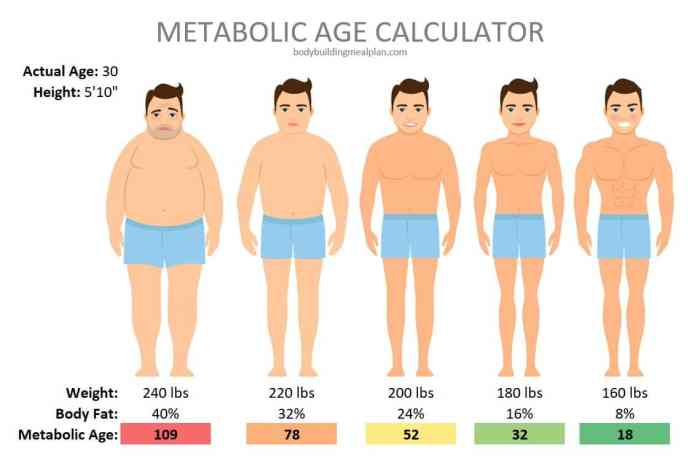
Basal metabolic rate, or BMR, refers to the amount of energy our bodies expend at rest. As we age, our BMR tends to decline, which means we burn fewer calories even when we’re not actively exercising. This decrease in BMR is partly due to the loss of muscle mass, as muscle tissue is metabolically active.
Additionally, age-related changes in body composition, such as the shift from lean mass to fat mass, can also contribute to a lower BMR.
Body Composition
With advancing age, our body composition undergoes significant changes. We tend to lose muscle mass and gain body fat, which can have implications for our metabolism. Muscle mass is metabolically active, meaning it burns calories even at rest. Therefore, a decline in muscle mass can lead to a reduction in BMR.
On the other hand, body fat is less metabolically active, so an increase in body fat percentage can further contribute to a lower BMR.
Dietary Modifications
As we age, our metabolism naturally slows down, making it essential to adjust our dietary habits to maintain optimal health. Here are some key dietary modifications recommended for individuals over 40:
Calorie Intake
Calorie needs decrease with age due to reduced physical activity and muscle mass. Aim for a calorie intake that supports a healthy weight and prevents weight gain. Consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine your personalized calorie requirements.
Macronutrient Distribution
Focus on consuming a balanced distribution of macronutrients:
- Protein:Protein is crucial for maintaining muscle mass and supporting metabolism. Aim for 1.2-1.7 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day.
- Carbohydrates:Choose whole grains, fruits, and vegetables for fiber and sustained energy. Limit processed and sugary carbohydrates.
- Fats:Include healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil. Avoid unhealthy saturated and trans fats.
Hydration
Staying hydrated is essential for overall health and metabolism. Aim to drink eight glasses of water per day, or more if you engage in physical activity.
Specific Nutrients
In addition to macronutrients, certain nutrients play a vital role in supporting metabolism:
- Fiber:Fiber helps regulate blood sugar levels, promotes satiety, and supports a healthy digestive system.
- Antioxidants:Antioxidants protect cells from damage and may help boost metabolism. Include antioxidant-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in your diet.
Key Dietary Recommendations for Individuals Over 40
| Nutrient | Recommended Intake |
|---|---|
| Calories | Personalized based on age, activity level, and weight |
| Protein | 1.2-1.7 grams per kilogram of body weight per day |
| Carbohydrates | Choose whole grains, fruits, and vegetables |
| Fats | Include healthy fats from avocados, nuts, and olive oil |
| Fiber | Aim for 25-30 grams per day |
| Antioxidants | Include antioxidant-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains |
Exercise Regimen
As we age, our metabolism slows down, making it more challenging to maintain a healthy weight and overall well-being. However, incorporating regular exercise into our routine can help mitigate this decline and improve our health. Here’s how to design an exercise plan tailored to individuals over 40:
Exercise Types and Benefits
Different types of exercise offer unique benefits for metabolism and overall health:
- Cardio:Improves cardiovascular health, burns calories, and boosts metabolism. Opt for low-impact activities like swimming, cycling, or walking; gradually increase intensity and duration.
- Strength Training:Builds muscle mass, strengthens bones, and increases metabolism. Focus on compound exercises (e.g., squats, push-ups) using lighter weights and higher repetitions.
- Flexibility:Improves range of motion, reduces risk of injury, and aids in balance. Incorporate stretching and yoga into your routine; hold stretches for 15-30 seconds.
Exercise Recommendations
Tailor your exercise plan to your fitness level and goals: Beginner:Start with 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. Gradually increase duration and intensity as you get stronger. Intermediate:Aim for 60 minutes of moderate-to-vigorous exercise most days of the week.
As we age over 40, our metabolism changes, making it more difficult to maintain a healthy weight. Maintaining weight loss after 40 requires a holistic approach that includes regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep. Understanding these metabolic changes is crucial for developing effective weight management strategies that address the unique challenges faced by individuals over 40.
Include a mix of cardio, strength training, and flexibility exercises. Advanced:Engage in high-intensity interval training (HIIT) or other challenging activities. Incorporate rest days into your schedule to allow for recovery.
Rest and Recovery
Rest is crucial for muscle growth and injury prevention. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep each night and allow for at least one rest day per week. Listen to your body and take breaks when needed.
Consistency and Progression
Consistency is key to achieving optimal results. Gradually increase the intensity, duration, or frequency of your workouts over time. This progressive overload principle challenges your body and promotes continued improvement.
Lifestyle Habits
As we age, our metabolism slows down, and our bodies become less efficient at burning calories. This can lead to weight gain and other health problems. However, there are several lifestyle habits that we can adopt to help boost our metabolism and improve our overall health.
Sleep
Getting enough sleep is essential for overall health, including metabolism. When we sleep, our bodies produce hormones that help to regulate metabolism. Getting less than seven hours of sleep per night can disrupt these hormones and lead to weight gain.
- Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night.
- Establish a regular sleep schedule and stick to it as much as possible, even on weekends.
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine to help you fall asleep more easily.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can lead to weight gain by increasing levels of the stress hormone cortisol. Cortisol can cause the body to store fat, especially around the abdomen.
- Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, yoga, or meditation.
- Get regular massages or acupuncture to help reduce stress levels.
- Talk to a therapist or counselor if you are struggling to manage stress on your own.
Smoking Cessation
Smoking is one of the worst things you can do for your metabolism. Nicotine can increase your heart rate and blood pressure, which can lead to weight gain. Quitting smoking can help you to boost your metabolism and improve your overall health.
- Set a quit date and stick to it.
- Use nicotine replacement therapy or other medications to help you quit.
- Join a support group or talk to a therapist to help you stay motivated.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for overall health, including metabolism. Being overweight or obese can slow down your metabolism and make it more difficult to lose weight. Losing even a small amount of weight can help to boost your metabolism and improve your health.
- Eat a healthy diet and exercise regularly.
- Set realistic weight loss goals and don’t get discouraged if you don’t reach them overnight.
- Talk to your doctor or a registered dietitian if you need help with weight loss.
Avoiding Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Drinking alcohol in moderation is not harmful to your health, but drinking too much alcohol can lead to weight gain. Alcohol is high in calories, and it can also interfere with your metabolism. If you are trying to lose weight or improve your overall health, it is important to avoid excessive alcohol consumption.
- Limit your alcohol intake to one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men.
- Avoid binge drinking.
- Choose low-calorie alcoholic beverages, such as light beer or wine.
Medical Conditions
As we age, our bodies undergo various physiological changes that can affect our metabolism. Certain medical conditions can also contribute to metabolic changes in individuals over 40. Understanding these conditions and their impact on metabolism is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being.
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. This hormone is responsible for regulating metabolism, energy levels, and body temperature. Symptoms of hypothyroidism include fatigue, weight gain, constipation, dry skin, and sensitivity to cold. Diagnosis involves a blood test to measure thyroid hormone levels.
Treatment typically involves thyroid hormone replacement therapy, which can help improve metabolism and alleviate symptoms.
Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels. Over time, uncontrolled diabetes can damage blood vessels and nerves, leading to complications such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease. There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder in which the body does not produce insulin, a hormone that helps glucose enter cells for energy.
Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body does not produce enough insulin or does not use insulin effectively. Symptoms of diabetes include frequent urination, increased thirst, weight loss, and fatigue. Diagnosis involves blood tests to measure blood sugar levels. Treatment for diabetes involves managing blood sugar levels through medication, diet, and exercise.
Cushing’s Syndrome
Cushing’s syndrome is a condition caused by prolonged exposure to high levels of cortisol, a hormone produced by the adrenal glands. Cortisol helps regulate metabolism, blood pressure, and immune function. Symptoms of Cushing’s syndrome include weight gain, high blood pressure, diabetes, and muscle weakness.
Diagnosis involves blood and urine tests to measure cortisol levels. Treatment options include medication to reduce cortisol production or surgery to remove a tumor on the adrenal glands.
Metabolic Disorders
Metabolic disorders, such as obesity, diabetes, and thyroid dysfunction, are becoming increasingly prevalent among individuals over 40. These disorders can have a significant impact on overall health and well-being, affecting energy levels, weight management, and even increasing the risk of developing other chronic diseases.
Prevalence and Risk Factors
Obesity, characterized by excessive body fat, is a major concern for individuals over 40. The prevalence of obesity increases with age, with approximately 70% of individuals over 65 being overweight or obese. Risk factors for obesity include unhealthy diet, lack of physical activity, and genetic predisposition.Diabetes
is another common metabolic disorder that affects individuals over 40. The risk of developing diabetes increases with age, and it is estimated that over 25% of individuals over 65 have diabetes. Risk factors for diabetes include obesity, family history, and certain lifestyle factors such as poor diet and lack of exercise.Thyroid
dysfunction, which involves an imbalance in thyroid hormone production, is also more common among individuals over 40. The most common type of thyroid dysfunction is hypothyroidism, which occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. Risk factors for thyroid dysfunction include autoimmune disorders, certain medications, and iodine deficiency.
Impact on Health
Metabolic disorders can have a significant impact on overall health and well-being. Obesity can increase the risk of developing heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Diabetes can damage blood vessels and nerves, leading to complications such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness.
Thyroid dysfunction can affect metabolism, weight management, and mood, and can also increase the risk of developing heart disease and other health problems.
Screening, Prevention, and Management, Metabolism changes over 40
Regular screening is important for early detection and management of metabolic disorders. Screening tests for obesity include body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference measurements. Screening tests for diabetes include fasting blood glucose and hemoglobin A1c tests. Screening tests for thyroid dysfunction include thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and free thyroxine (T4) tests.Prevention
of metabolic disorders involves adopting healthy lifestyle habits, such as maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and following a balanced diet. Management of metabolic disorders often involves lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise modifications, as well as medication or other treatments as recommended by a healthcare professional.
Supplements and Medications
As we age, our metabolism naturally slows down. While lifestyle changes are crucial, supplements and medications can provide additional support. Let’s explore their role and evidence-based recommendations.
Green Tea Extract
Green tea extract contains catechins, antioxidants that may boost metabolism. Studies suggest:
- Dosage:250-500mg daily
- Duration:12 weeks or longer
- Benefits:Increased fat oxidation, improved insulin sensitivity
- Limitations:May interfere with iron absorption, caffeine sensitivity
Turmeric
Turmeric contains curcumin, a compound with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Research indicates:
- Dosage:500-1000mg daily
- Duration:8-12 weeks
- Benefits:Reduced inflammation, improved cholesterol levels
- Limitations:May interact with blood thinners
Metabolic Medications
Certain medications can help manage metabolic disorders and improve metabolism. Common medications include:
- Metformin
- Orlistat
- Phentermine
These medications have potential side effects and drug interactions:
- Drug-drug interactions:May interact with blood thinners, antihypertensives
- Common side effects:Nausea, diarrhea, headaches
Personalized Approach
Metabolism management isn’t a one-size-fits-all approach. Factors like genetics and lifestyle can influence your unique metabolic profile. Working with healthcare professionals can help you develop a tailored plan that meets your specific needs and goals.
Hey there, lovely lady! As we gracefully navigate our 40s, our metabolism might be throwing us a few curveballs. But fear not! Dive into Weight loss success stories for women over 40 and get inspired by those who’ve triumphed over similar metabolic challenges.
Their journeys can empower us to embrace our bodies and adapt to the changes that come with age, proving that metabolism changes over 40 don’t have to hold us back.
Factors Influencing Metabolic Profiles
- Genetics: Your genes play a role in determining your metabolic rate and how your body processes nutrients.
- Age: Metabolism naturally slows down as we age.
- Muscle mass: Muscle burns more calories than fat, so having more muscle can boost your metabolism.
- Hormonal changes: Hormones like thyroid hormone and estrogen can affect metabolism.
- Lifestyle factors: Diet, exercise, and sleep habits can all influence metabolism.
Developing a Tailored Plan with Healthcare Professionals
To create a personalized plan, consider these steps:
- Consult with a registered dietitian or doctor to discuss your health history, lifestyle, and goals.
- Get a comprehensive metabolic assessment to measure your resting metabolic rate and other key indicators.
- Based on the assessment results, work with your healthcare team to develop a personalized nutrition and exercise plan.
- Monitor your progress regularly and make adjustments as needed.
Technology and Tracking: Metabolism Changes Over 40
Technology plays a significant role in monitoring metabolism and tracking progress towards metabolic health goals. Wearable devices like fitness trackers and smartwatches can monitor steps taken, calories burned, and heart rate. Fitness apps can track food intake, water consumption, and sleep patterns.
Online platforms offer personalized dashboards and progress reports, providing a comprehensive view of metabolic health.
Data Analysis for Optimization
Data collected from these technologies can be analyzed to identify patterns and trends. This information can help individuals optimize their metabolic health strategies by adjusting diet, exercise, and lifestyle habits. For example, tracking calorie intake and activity levels can help determine the optimal calorie deficit for weight loss.
Monitoring sleep patterns can identify areas for improvement, leading to better rest and hormonal balance, both crucial for metabolic health.
– Mindfulness and Motivation
Maintaining metabolic health over 40 requires a combination of physical and mental strategies. Mindfulness and motivation play a crucial role in this journey, helping you develop a positive mindset, stay focused on your goals, and overcome challenges.
Mindfulness involves paying attention to the present moment without judgment. By practicing mindfulness, you can reduce stress, improve focus, and increase self-awareness. These qualities are essential for maintaining a healthy metabolism and making sustainable lifestyle changes.
Guided Meditation
Take a few minutes to practice this guided meditation:
- Find a comfortable place to sit or lie down.
- Close your eyes and take a few deep breaths.
- Bring your attention to your body and notice any sensations you feel.
- If your mind wanders, gently bring it back to the present moment.
- Continue meditating for 5-10 minutes.
This meditation helps you cultivate mindfulness and reduce stress, which can support your metabolic health.
Goal Setting and Tracking
Setting realistic goals is essential for staying motivated. Break down your long-term goals into smaller, manageable steps. Celebrate your successes along the way to maintain momentum.
Journaling is a powerful tool for self-reflection and goal tracking. Regularly record your thoughts, feelings, and progress. This practice helps you stay accountable, identify areas for improvement, and appreciate your journey.
Community and Support
Navigating metabolism changes over 40 can be challenging, but you don’t have to go it alone. Joining support groups or online communities can provide invaluable benefits, including:
Benefits of Support Groups
- Sharing experiences, tips, and encouragement
- Fostering accountability and support
- Reducing feelings of isolation and loneliness
- Improving overall well-being
Finding Support Groups
Local support groups can be found through community centers, hospitals, and health organizations. Virtual support groups can be found on platforms like Meetup, Facebook, and Reddit.
Research on Support Groups
Research has shown that support groups can significantly improve the health and well-being of older adults. For example, a study published in the Journal of Gerontology found that older adults who participated in support groups had improved physical and mental health, as well as increased social engagement.
Specific Examples
Here are a few examples of how support groups have helped individuals over 40:
- One woman joined a support group for women over 40 who were struggling with weight gain and hormonal changes. She found solace in sharing her experiences and receiving encouragement from others who understood what she was going through.
- A man joined a virtual support group for older adults with diabetes. He found it helpful to connect with others who were facing similar challenges and to learn about new ways to manage his condition.
Types of Support Groups
There are many different types of support groups available, including:
- In-person support groups
- Virtual support groups
- Specialized support groups for specific topics or populations
Educational Resources
Understanding the metabolic changes that occur over 40 requires access to reliable and evidence-based information. Here’s a comprehensive list of reputable sources to guide you:
Websites
- National Institute on Aging (NIA): https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/metabolism-and-aging
- Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics: https://www.eatright.org/health/wellness/healthy-aging/metabolism-and-aging
- Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health: https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/metabolism-and-aging/
Books
- “The Metabolism Solution: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight Loss and Lifelong Health” by Haylie Pomroy
- “The Aging Metabolism: How to Eat, Exercise, and Supplement for Lifelong Vitality” by Stephen Holt
- “Metabolism Reset: A Science-Based Guide to Optimizing Your Metabolism and Revitalizing Your Health” by Luiza Petre
Articles
- “Metabolism and Aging: What You Need to Know” by Harvard Health Publishing: https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/metabolism-and-aging
- “How to Boost Your Metabolism After 40” by WebMD: https://www.webmd.com/diet/features/boost-metabolism-after-40
- “The Best Way to Boost Metabolism After 40” by U.S. News & World Report: https://health.usnews.com/health-news/best-diet/articles/how-to-boost-metabolism-after-40
Organizations
- American Diabetes Association: https://www.diabetes.org/
- American Heart Association: https://www.heart.org/
- National Osteoporosis Foundation: https://www.nof.org/
Remember to always evaluate the credibility and reliability of online health information by considering the source, the author’s qualifications, the presence of references, and any potential biases or conflicts of interest.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Read inspiring stories of individuals who have successfully managed metabolism changes over 40. Learn from their real-life experiences, effective strategies, and lifestyle modifications. Discover the power of perseverance and the importance of seeking professional support when needed.
Sarah’s Journey
Sarah, a 45-year-old woman, struggled with weight gain and fatigue. After consulting a doctor, she realized her metabolism had slowed down with age. She embarked on a journey of lifestyle changes, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management techniques.
Within six months, she lost 20 pounds and regained her energy levels.
As we pass the big 4-0, our metabolism takes a bit of a backseat. This can make losing weight a bit more challenging. However, there are some things we can do to help, such as making sure we’re getting enough protein and fiber.
We should also be mindful of our hormone levels, as changes in these can also affect our weight. You can read more about Weight loss after 40 female hormone changes here. Getting regular exercise is also important, as it can help to boost our metabolism and burn calories.
So, if you’re over 40 and looking to lose weight, don’t despair! There are plenty of things you can do to reach your goals.
John’s Transformation
John, a 50-year-old man, was diagnosed with prediabetes. He was determined to reverse his condition and improve his health. He consulted a registered dietitian and created a personalized meal plan that supported his metabolic needs. John also joined a gym and incorporated daily walks into his routine.
In one year, he reduced his blood sugar levels and lost 30 pounds.
The Importance of Professional Support
While many individuals can manage metabolism changes on their own, others may benefit from professional support. Registered dietitians, certified personal trainers, and healthcare providers can provide personalized guidance, motivation, and accountability. Seeking professional help can increase the chances of success and long-term sustainability.
Research Updates
Stay informed about the latest scientific breakthroughs and advancements in metabolism management. We’ll delve into emerging trends, cutting-edge technologies, and promising therapies that are reshaping our understanding and treatment of metabolism changes over 40.
Ongoing research continues to unravel the complexities of metabolism and its impact on our health. By keeping abreast of these advancements, we can empower ourselves with the knowledge and tools necessary to optimize our metabolic well-being.
Precision Medicine and Personalized Interventions
- Precision medicine is revolutionizing metabolism management by tailoring treatments to individual genetic profiles and lifestyle factors.
- Personalized interventions, based on genetic testing and detailed metabolic assessments, are optimizing outcomes and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
Last Recap
Remember, metabolism changes over 40 are not a hindrance but an opportunity for self-discovery and renewal. By understanding the underlying mechanisms and implementing the strategies discussed in this guide, you can harness the power of your metabolism to maintain a healthy weight, boost your energy levels, and age gracefully.
Embrace this journey as a chance to redefine your relationship with your body and live your best life, one vibrant step at a time.
Key Questions Answered
How can I boost my metabolism over 40?
Incorporating regular exercise, focusing on a balanced diet rich in protein and fiber, and getting adequate sleep are effective ways to enhance your metabolism.
What are the key hormonal changes that affect metabolism over 40?
Declining levels of sex hormones, such as estrogen and testosterone, can impact metabolic rate and body composition.
How does stress affect metabolism?
Chronic stress can lead to hormonal imbalances that disrupt metabolism, making it harder to maintain a healthy weight.
What are some common medical conditions that can affect metabolism over 40?
Conditions like thyroid dysfunction, diabetes, and obesity can influence metabolic processes and require appropriate medical management.
How can I track my progress and stay motivated?
Utilizing fitness trackers, setting realistic goals, and joining support groups can help you monitor your progress and stay accountable.