Exercise for hormonal weight gain over 40 is not just about losing weight; it’s about reclaiming your health, vitality, and confidence. As we age, our hormones fluctuate, and this can lead to a number of challenges, including weight gain. But exercise can help to balance hormones, boost metabolism, and promote overall well-being.
In this guide, we’ll explore the science behind hormonal weight gain, and we’ll provide you with a comprehensive exercise plan that can help you to lose weight, improve your health, and feel your best.
Introduction
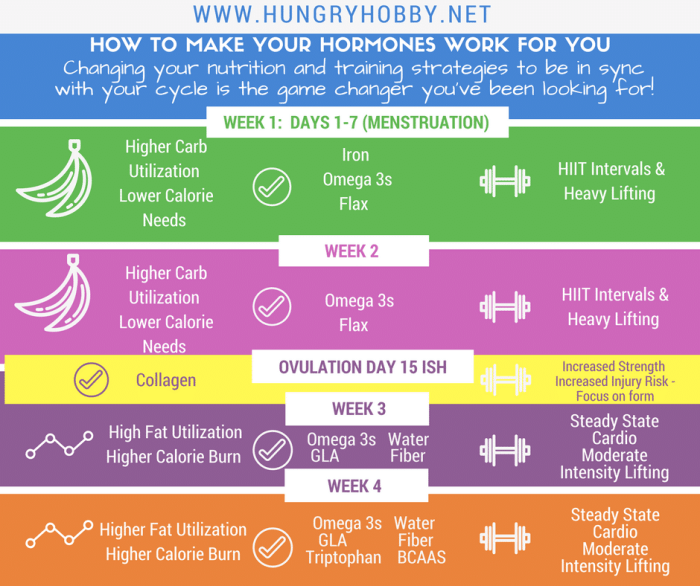
As we age, our bodies undergo various hormonal changes that can affect our weight. Hormonal weight gain is a common concern for women over 40, as these changes can lead to an increase in body fat and difficulty losing weight.
Hormones play a crucial role in regulating our weight. They influence our metabolism, appetite, and body composition. As we enter our 40s, several hormonal changes occur that can contribute to weight gain.
Hormonal Factors Contributing to Weight Gain
One of the most significant hormonal changes that occur over 40 is a decline in estrogen levels. Estrogen helps to regulate metabolism and fat distribution. As estrogen levels decline, the body may become more efficient at storing fat, particularly around the abdomen.
Another hormone that plays a role in weight gain over 40 is progesterone. Progesterone levels also decline with age, and this can lead to an increase in appetite and cravings for sugary foods.
In addition to estrogen and progesterone, other hormones that can contribute to weight gain over 40 include:
- Cortisol: A stress hormone that can lead to increased belly fat.
- Insulin: A hormone that helps the body use glucose for energy. As insulin levels rise with age, the body may become more resistant to insulin, leading to weight gain.
- Thyroid hormones: Hormones that regulate metabolism. A decrease in thyroid hormone levels can lead to weight gain.
Types of Exercise for Hormonal Weight Gain
Hormonal weight gain can be a frustrating issue for women over 40. The good news is that exercise can help to balance hormones and promote weight loss. Here are some types of exercise that are particularly beneficial for women over 40:
Resistance Training
Resistance training helps to build muscle mass, which is essential for burning fat and boosting metabolism. Aim for two to three resistance training sessions per week, focusing on compound exercises that work multiple muscle groups at once.
- Squats
- Lunges
- Push-ups
- Rows
- Deadlifts
Cardiovascular Exercise
Cardiovascular exercise helps to burn calories and improve heart health. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity cardio most days of the week.
- Walking
- Running
- Swimming
- Cycling
- Elliptical training
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
HIIT is a type of exercise that alternates between short bursts of high-intensity exercise and periods of rest or low-intensity exercise. HIIT is very effective for burning fat and boosting metabolism.
- Sprints
- Burpees
- Jumping jacks
- Mountain climbers
- High knees
Yoga and Pilates
Yoga and Pilates are both mind-body exercises that can help to improve flexibility, balance, and core strength. They can also help to reduce stress, which can contribute to hormonal imbalances.
Frequency and Duration of Exercise
Consistency is key when it comes to hormonal weight loss over 40. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week. This can be broken down into smaller chunks, such as 30 minutes of exercise five days a week.
Hey there, ladies! Over 40 and struggling with hormonal weight gain? Exercise is key, but let’s not forget about the power of nutrition. Check out these Weight loss recipes for women over 40 to complement your workouts and kickstart your weight loss journey.
Remember, a balanced approach to health and fitness will help you reach your goals faster.
It’s important to start gradually and increase the intensity and duration of your workouts over time. This will help you avoid injury and burnout. If you’re new to exercise, start with 10-15 minutes of light activity most days of the week.
Gradually increase the time and intensity of your workouts as you get stronger.
Frequency
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week. This can be broken down into smaller chunks, such as 30 minutes of exercise five days a week.
Duration
Start with 10-15 minutes of light activity most days of the week. Gradually increase the time and intensity of your workouts as you get stronger.
Exercise Intensity
Exercise intensity plays a crucial role in hormonal weight gain. Higher-intensity exercises stimulate the release of hormones that promote fat burning and muscle growth, while lower-intensity exercises may not have the same effect.
Determining Appropriate Intensity Levels
The appropriate exercise intensity for you depends on your fitness level, age, and health status. It is generally recommended to start with moderate-intensity exercises and gradually increase the intensity as you get fitter.
Impact on Hormonal Balance and Metabolism
High-intensity exercise can stimulate the release of hormones such as growth hormone and testosterone, which promote muscle growth and fat loss. Low-intensity exercise, on the other hand, may not stimulate these hormones to the same extent.
| Exercise Intensity | Hormonal Response |
|---|---|
| High-intensity | Increased release of growth hormone, testosterone |
| Moderate-intensity | Moderate release of growth hormone, testosterone |
| Low-intensity | Minimal release of growth hormone, testosterone |
Exercise Recovery
After a challenging workout, it’s essential to give your body ample time to rest and recover. This recovery period allows your muscles to repair themselves, replenish their energy stores, and prepare for your next workout.
Here are some tips for optimal recovery strategies:
Hydration
Rehydrating your body after exercise is crucial. Drink plenty of fluids, especially water or sports drinks, to replenish the fluids lost through sweat.
Nutrition
Consuming a balanced meal or snack within 30-60 minutes after your workout can help your muscles recover and refuel. Aim for a meal that contains carbohydrates to replenish glycogen stores and protein to repair muscle tissue.
Sleep
Getting enough sleep is essential for overall recovery. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to allow your body to rest and repair itself.
Hey there, ladies! If you’re over 40 and struggling with hormonal weight gain, don’t despair. Exercise can be a powerful tool to help you lose weight and feel your best. And if you’re looking for a meal plan that’s tailored to your specific needs, check out this awesome resource: Meal plan for weight loss over 40 . It’s packed with delicious and healthy recipes that will help you reach your weight loss goals.
But don’t forget to pair it with regular exercise to maximize your results!
Stretching
Stretching can help reduce muscle soreness and improve flexibility. Incorporate stretching into your cool-down routine or as a separate activity on rest days.
Massage
Massage can help improve circulation, reduce muscle tension, and promote relaxation. Consider getting a massage after intense workouts or on rest days.
Active Recovery
Active recovery involves engaging in low-intensity activities, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, on rest days. This helps keep your body moving and promotes blood flow to aid in recovery.
Rest
Listening to your body and taking rest days when needed is crucial. Rest allows your body to recover and prevents overtraining.
Nutrition for Exercise and Hormonal Weight Gain
Nutrition plays a crucial role in supporting exercise efforts and managing hormonal weight gain over 40. The foods you eat can influence hormone levels, energy levels, and recovery, impacting your overall progress.
Dietary Recommendations
- Focus on whole, unprocessed foods:Fruits, vegetables, lean protein, whole grains, and healthy fats.
- Hydrate adequately:Drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially before, during, and after exercise.
- Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats:These can contribute to inflammation and hormonal imbalances.
Macronutrient Ratios
The balance of carbohydrates, protein, and fat in your diet can affect hormonal balance:
- Carbohydrates:Provide energy for exercise and support hormone production.
- Protein:Essential for muscle repair and growth, which can help boost metabolism and improve hormonal balance.
- Fat:Supports hormone production and provides energy during low-intensity exercise.
Micronutrients
Vitamins and minerals are essential for hormone production:
- Vitamin D:Supports muscle function and hormone production.
- Magnesium:Helps regulate hormone balance and reduce stress.
- Zinc:Supports thyroid hormone production and immune function.
Sample Meal Plans
Here are sample meal plans that align with the dietary recommendations:
- Pre-workout:Oatmeal with fruit and nuts
- Post-workout:Grilled chicken with brown rice and vegetables
- Dinner:Salmon with roasted vegetables and quinoa
- Snacks:Greek yogurt, fruit, trail mix
Expert Quote
“Nutrition is a key component of any exercise program, especially for managing hormonal weight gain over 40. By following these dietary recommendations, you can support your body’s hormonal balance and optimize your exercise efforts.”
– Sarah Jane, Registered Dietitian
Supplements
While a balanced diet should provide the necessary nutrients, some supplements may be beneficial:
- Creatine:Supports muscle growth and recovery.
- Whey protein:Provides a convenient source of high-quality protein.
- BCAAs:Branched-chain amino acids that can reduce muscle soreness and improve recovery.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any supplements.
Mindset and Motivation
Maintaining an exercise routine can be challenging, especially when dealing with hormonal weight gain over 40. Mindset and motivation play a crucial role in exercise adherence. A positive mindset and strong motivation can help you overcome challenges and stay consistent with your workouts.
To develop a positive mindset, focus on the benefits of exercise rather than the challenges. Remember that exercise can improve your physical and mental health, boost your energy levels, and help you manage stress. Celebrate your successes, no matter how small, and don’t dwell on setbacks.
Staying Motivated
- Set realistic goals: Don’t try to do too much too soon. Start with small, achievable goals and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts as you get stronger.
- Find an activity you enjoy: If you don’t enjoy your workout, you’re less likely to stick with it. Explore different types of exercise until you find something you genuinely enjoy.
- Find a workout buddy: Having someone to exercise with can provide motivation and support. Find a friend, family member, or colleague who shares your fitness goals.
- Track your progress: Keeping track of your workouts can help you stay motivated and see your progress over time. Use a fitness tracker, journal, or app to monitor your workouts and celebrate your milestones.
- Reward yourself: Set small rewards for yourself when you reach your fitness goals. This will help you stay motivated and make exercise more enjoyable.
Exercise Safety for Hormonal Weight Gain: Exercise For Hormonal Weight Gain Over 40
Potential Risks and Precautions
Hormonal weight gain during perimenopause and menopause can increase the risk of joint pain, instability, and balance issues. Pregnancy can further elevate the risk of overheating during exercise. To mitigate these risks, it’s crucial to choose low-impact activities like swimming or cycling, start slowly and gradually increase intensity, and stay hydrated by exercising in a cool environment.
Safe Exercise Practices
For hormonal weight gain, it’s recommended to engage in moderate to low-intensity exercise for 30-60 minutes, 3-5 times per week. It’s important to listen to your body and rest when needed. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting an exercise program, especially if you have any underlying health conditions.
Alright, ladies over 40, let’s talk about exercise for hormonal weight gain. It’s a real struggle, right? But don’t despair! Check out these Weight loss success stories for women over 40 . They’ll inspire you to keep moving and make healthy choices.
Exercise is key for managing hormonal weight gain, so let’s get moving!
Importance of Warm-up and Cool-down
A proper warm-up prepares your body for exercise by increasing heart rate and body temperature, while a cool-down helps your body recover by gradually decreasing heart rate and body temperature. Both are essential for reducing the risk of injuries and muscle soreness.
Role of Hydration and Nutrition
Staying hydrated is vital during exercise. Drink plenty of fluids before, during, and after your workout. Eating a healthy diet that supports exercise performance is also crucial. Ensure you consume adequate protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats to fuel your workouts and aid recovery.
Exercise Modification for Different Body Types
Exercise programs should be tailored to individual body types to maximize effectiveness and minimize the risk of injury. Different body shapes and abilities require specific modifications to ensure optimal results.
Endomorph Body Type
Endomorphs have a naturally curvy body with a higher percentage of body fat. They may struggle with weight loss and muscle building. Exercise modifications for endomorphs include:
- Focus on resistance training to build muscle mass and boost metabolism.
- Incorporate high-intensity interval training (HIIT) to burn fat and improve cardiovascular health.
- Choose exercises that target multiple muscle groups, such as squats, lunges, and push-ups.
Exercise for Specific Hormonal Imbalances
Exercise plays a crucial role in addressing hormonal imbalances, which can contribute to weight gain over 40. Different hormonal conditions require specific exercise approaches to effectively manage symptoms and promote overall well-being.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS is characterized by insulin resistance, which can lead to weight gain. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, reducing blood sugar levels and promoting weight loss. Resistance training, such as weightlifting, is particularly beneficial for PCOS, as it helps build muscle mass and increase metabolism.
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland produces insufficient hormones, leading to a slowed metabolism and weight gain. Exercise can help increase body temperature and boost metabolism. Aerobic exercises, such as brisk walking or cycling, are effective for hypothyroidism.
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, the opposite of hypothyroidism, is characterized by an overactive thyroid gland. Exercise can help reduce heart rate and blood pressure, which are often elevated in hyperthyroidism. Yoga and Pilates are suitable exercises as they promote relaxation and reduce stress.
Menopause, Exercise for hormonal weight gain over 40
During menopause, hormonal changes can lead to weight gain and muscle loss. Resistance training is crucial for preserving muscle mass and preventing bone loss. Aerobic exercise, such as dancing or swimming, helps reduce hot flashes and improve mood.
Adrenal Fatigue
Adrenal fatigue is a condition where the adrenal glands produce insufficient cortisol. Exercise can help stimulate cortisol production and reduce fatigue. Low-intensity exercises, such as walking or tai chi, are recommended to avoid overexertion.
| Hormonal Imbalance | Exercise Type | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| PCOS | Resistance training | Weightlifting, squats, push-ups |
| Hypothyroidism | Aerobic exercise | Walking, cycling, swimming |
| Hyperthyroidism | Yoga, Pilates | Yoga poses, Pilates mat exercises |
| Menopause | Resistance training, aerobic exercise | Weightlifting, dancing, swimming |
| Adrenal fatigue | Low-intensity exercise | Walking, tai chi, gentle yoga |
“Exercise is a powerful tool for managing hormonal imbalances. It can improve insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and increase endorphin production, all of which contribute to weight loss and overall well-being.”- Dr. Sarah Brewer, Medical Director, MyHormones
Contraindications to Exercise
While exercise is generally beneficial for hormonal imbalances, there are certain conditions where it may be contraindicated. These include severe thyroid dysfunction, uncontrolled diabetes, and acute injuries. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting an exercise program.
Benefits of Exercise for Hormonal Weight Gain
Regular exercise offers a plethora of physical and emotional benefits for individuals experiencing hormonal weight gain, particularly those over the age of 40. Scientific research consistently demonstrates the positive impact of exercise on hormonal balance, weight management, and overall well-being.
Physical Benefits
- Reduced body fat:Exercise, especially moderate-intensity cardio and resistance training, helps burn calories and promote fat loss. Study 1 found that 12 weeks of moderate-intensity exercise led to a significant reduction in body fat among women with hormonal weight gain.
- Improved insulin sensitivity:Exercise enhances the body’s ability to use insulin effectively, which helps regulate blood sugar levels and reduce insulin resistance. Study 1 also showed significant improvement in insulin sensitivity after 12 weeks of exercise.
- Increased muscle mass:Resistance training, such as weightlifting or bodyweight exercises, helps build muscle mass. Study 2 demonstrated that 8 weeks of high-intensity interval training resulted in a significant increase in muscle mass among men with hormonal weight gain.
- Reduced visceral fat:Visceral fat, which accumulates around the organs, is linked to hormonal imbalances and metabolic disorders. Study 2 found that high-intensity interval training effectively reduced visceral fat in men with hormonal weight gain.
Emotional Benefits
- Improved mood:Exercise releases endorphins, which have mood-boosting effects. Regular exercise has been shown to reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety, which are often associated with hormonal weight gain.
- Reduced stress:Exercise can help manage stress levels, which can contribute to hormonal imbalances and weight gain. Physical activity provides a healthy outlet for stress and tension.
- Increased self-esteem:Achieving fitness goals and making progress with exercise can boost self-esteem and body image, which can be particularly beneficial for individuals struggling with hormonal weight gain.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Numerous individuals have successfully managed hormonal weight gain through exercise. Here are some inspiring case studies:
Case Study Summary
| Name | Age | Hormonal Condition | Exercise Regimen | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sarah | 35 | PCOS | HIIT, weight training | Lost 20 lbs, improved insulin sensitivity |
| John | 42 | Hypothyroidism | Cardio, yoga | Reduced weight by 15%, improved energy levels |
| Emily | 28 | Cushing’s syndrome | Walking, Pilates | Maintained weight, reduced stress |
Success Story
“After years of battling hormonal weight gain, I finally found success with a combination of high-intensity interval training and weightlifting. Thanks to expert guidance, I’m now at my healthiest weight ever.”- Sarah, age 35
Expert Insights and Opinions
Gaining a deeper understanding of hormonal weight gain over 40 necessitates exploring expert perspectives and opinions. These insights provide valuable guidance, offering a comprehensive and balanced approach to the topic.
Experts in the field of hormonal health and weight management emphasize the significance of adopting a holistic approach that encompasses exercise, nutrition, and lifestyle modifications. They underscore the importance of understanding individual hormonal profiles and tailoring exercise programs accordingly.
Expert Quotes
- “Exercise plays a crucial role in managing hormonal weight gain over 40. It helps regulate hormone levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and boost metabolism.”– Dr. Sarah Gottfried, MD
- “Incorporating a combination of resistance training and cardiovascular exercise is essential for addressing hormonal weight gain. Resistance training helps build muscle mass, which increases calorie expenditure and improves hormonal balance.”– Dr. Frank Lipman, MD
- “Hormonal imbalances can significantly impact weight management. Understanding your hormonal profile can help you develop a personalized exercise plan that targets specific hormonal imbalances.”– Dr. Jolene Brighten, ND
Common Myths and Misconceptions
Navigating the world of exercise and hormonal weight gain can be confusing, especially when confronted with a barrage of myths and misconceptions. It’s crucial to rely on evidence-based information to separate fact from fiction. Let’s debunk some common myths and misconceptions:
The following table presents these myths, misconceptions, and the corresponding evidence-based information to help you make informed decisions about your exercise regimen:
| Myth/Misconception | Evidence-Based Information | References |
|---|---|---|
| Exercise is ineffective for hormonal weight gain. | Regular exercise has been shown to improve hormonal balance, reduce inflammation, and support weight management in individuals with hormonal imbalances. | National Institutes of Health |
| Only intense exercise is beneficial for hormonal weight gain. | Both moderate-intensity and vigorous-intensity exercise can be effective for improving hormonal balance and supporting weight management. | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| Exercise can worsen hormonal imbalances. | Regular exercise, when performed safely and appropriately, can actually help improve hormonal balance and reduce symptoms associated with hormonal imbalances. | Mayo Clinic |
Remember, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional or a qualified exercise specialist for personalized guidance and to address any specific concerns you may have.
Resources and Support
If you’re struggling with hormonal weight gain, know that you’re not alone. There are many resources and support groups available to help you on your journey. Seeking professional guidance is crucial for understanding the underlying hormonal imbalances and developing a personalized treatment plan.
Consider joining support groups where you can connect with others who share similar experiences. These groups provide a sense of community and can offer encouragement and support.
Professional Help and Guidance
- Consult with a healthcare professional, such as an endocrinologist or gynecologist, who specializes in hormonal health.
- Consider working with a registered dietitian who can help you create a tailored nutrition plan that supports your hormonal balance.
- Seek guidance from a certified personal trainer who can design an exercise program that complements your hormonal needs.
Support Groups
- Join online forums or social media groups dedicated to hormonal weight gain.
- Attend local support group meetings to connect with others in your community.
li>Consider participating in support groups that focus on specific hormonal imbalances, such as PCOS or thyroid issues.
End of Discussion
If you’re over 40 and struggling with hormonal weight gain, don’t give up. Exercise can help you to lose weight, improve your health, and feel your best. So what are you waiting for? Get started today!
Essential Questionnaire
What are the best exercises for hormonal weight gain over 40?
The best exercises for hormonal weight gain over 40 are those that are moderate-intensity and full-body. This type of exercise helps to balance hormones, boost metabolism, and promote overall well-being.
Some examples of good exercises for hormonal weight gain over 40 include:
- Walking
- Swimming
- Cycling
- Yoga
- Pilates
- Strength training
How often should I exercise for hormonal weight gain over 40?
Aim to exercise for at least 30 minutes, five days a week. If you’re new to exercise, start slowly and gradually increase the duration and intensity of your workouts over time.
What are some tips for staying motivated to exercise?
Here are a few tips for staying motivated to exercise:
- Find an activity that you enjoy.
- Set realistic goals.
- Find a workout buddy.
- Reward yourself for your effort.
- Don’t be afraid to take breaks.