Hormonal imbalance weight gain over 40 – As we navigate the hormonal shifts that accompany life’s fourth decade, understanding the impact of hormonal imbalance on weight gain becomes crucial. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate relationship between hormones, aging, and weight management, providing a roadmap to regain hormonal harmony and achieve a healthier weight.
Definition of Hormonal Imbalance and its Impact on Weight Gain
Hormonal imbalance is a condition in which the body produces too much or too little of a particular hormone. Hormones are chemical messengers that regulate various bodily functions, including metabolism, appetite, and weight.
When hormone levels are out of balance, it can lead to a variety of health problems, including weight gain. Some of the most common hormonal imbalances that can contribute to weight gain include:
Role of Hormones in Regulating Weight
- Estrogen:Estrogen is a hormone that is produced by the ovaries in women. It helps to regulate metabolism and appetite. When estrogen levels are low, it can lead to weight gain.
- Progesterone:Progesterone is another hormone that is produced by the ovaries in women. It helps to balance the effects of estrogen and prevent weight gain.
- Testosterone:Testosterone is a hormone that is produced by the testes in men and the ovaries in women. It helps to build muscle and burn fat. When testosterone levels are low, it can lead to weight gain.
- Thyroid hormone:Thyroid hormone is produced by the thyroid gland. It helps to regulate metabolism. When thyroid hormone levels are low, it can lead to weight gain.
- Cortisol:Cortisol is a hormone that is produced by the adrenal glands. It helps to regulate stress response. When cortisol levels are high, it can lead to weight gain.
Hormonal Changes Associated with Aging
As we age, our bodies undergo several hormonal changes that can contribute to weight gain. These changes are different for women and men, and they can have a significant impact on our metabolism, appetite, and body composition.
Changes in Women
- Decline in estrogen and progesterone:These hormones play a role in regulating metabolism and appetite. As estrogen levels decline, it can lead to a decrease in metabolism and an increase in appetite, which can contribute to weight gain.
- Increase in cortisol:This hormone is released in response to stress and can lead to increased appetite and weight gain.
- Changes in thyroid function:The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism. As we age, thyroid function can slow down, which can lead to weight gain.
Changes in Men
- Decline in testosterone:This hormone plays a role in muscle mass and metabolism. As testosterone levels decline, it can lead to a decrease in muscle mass and an increase in body fat.
- Increase in estrogen:Estrogen levels can increase slightly in men as they age, which can contribute to weight gain.
- Changes in thyroid function:As in women, thyroid function can slow down with age, leading to weight gain.
Common Symptoms of Hormonal Imbalance
Hormonal imbalance can manifest through a range of symptoms, including those related to weight gain. Here are some common indicators:
These symptoms can vary in severity and may not all be present in every individual experiencing hormonal imbalance.
Weight Gain and Body Composition Changes
- Difficulty losing weight despite following a healthy diet and exercise routine
- Accumulation of weight around the abdomen (central obesity)
- Changes in body composition, such as a decrease in muscle mass and an increase in body fat
Medical Conditions that Cause Hormonal Imbalance
Hormonal imbalances can be caused by a variety of medical conditions, including thyroid disorders, Cushing’s syndrome, and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). These conditions can disrupt the normal production and regulation of hormones, leading to weight gain and other symptoms.
Thyroid Disorders
Thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, can affect the production of thyroid hormones, which play a role in metabolism. Hypothyroidism, an underactive thyroid, can lead to weight gain, fatigue, and constipation. Hyperthyroidism, an overactive thyroid, can cause weight loss, anxiety, and increased heart rate.
Cushing’s Syndrome
Cushing’s syndrome is a condition caused by excessive production of the hormone cortisol. Cortisol can increase appetite and lead to weight gain, particularly in the face and abdomen. Other symptoms of Cushing’s syndrome include high blood pressure, diabetes, and muscle weakness.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS is a hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It is characterized by irregular menstrual cycles, high levels of androgens (male hormones), and the formation of cysts on the ovaries. PCOS can lead to weight gain, insulin resistance, and infertility.
Diagnostic Tests
Diagnosing medical conditions that cause hormonal imbalances typically involves a combination of physical exams, blood tests, and imaging tests. Blood tests can measure hormone levels, while imaging tests, such as ultrasounds or CT scans, can help identify structural abnormalities.
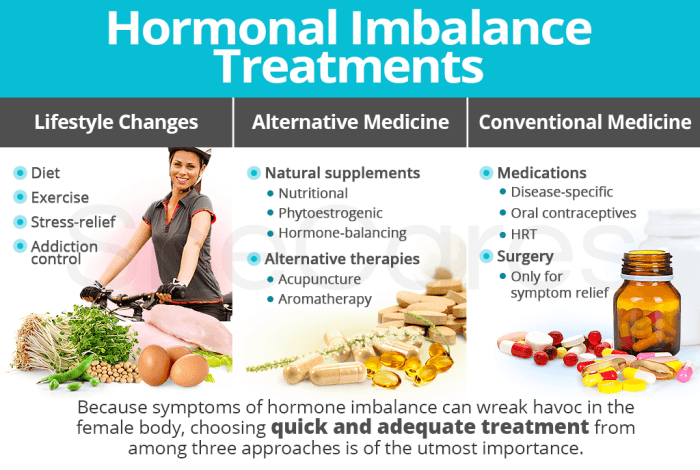
Treatment Options, Hormonal imbalance weight gain over 40
Treatment for medical conditions that cause hormonal imbalances depends on the underlying condition. Treatment options may include medication, surgery, or lifestyle changes. Medication can help regulate hormone levels, while surgery may be necessary to remove tumors or other abnormalities. Lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, can help manage symptoms and improve overall health.
Lifestyle Factors that Influence Hormonal Imbalance
Our lifestyle choices can significantly impact our hormonal balance. Maintaining a healthy weight, getting enough sleep, and managing stress are crucial for optimal hormone function. Let’s delve into specific lifestyle factors that can affect our hormones:
Diet
A balanced diet is essential for hormone production. Eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides the body with the nutrients it needs to make hormones. Avoiding processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive caffeine can help prevent hormonal imbalances.
Exercise
Regular exercise helps regulate hormone levels. Exercise can increase the production of endorphins, which have mood-boosting effects and can reduce stress hormones. It can also help maintain a healthy weight, which is important for hormone balance.
Sleep
Getting enough sleep is crucial for hormonal balance. When we sleep, our bodies produce hormones like melatonin and growth hormone, which play important roles in regulating metabolism and other bodily functions. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
Stress
Chronic stress can disrupt hormone production. When we are stressed, our bodies release hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can lead to weight gain and other health problems. Managing stress through techniques like yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature can help maintain hormonal balance.
Diagnosis of Hormonal Imbalance: Hormonal Imbalance Weight Gain Over 40
Pinpointing a hormonal imbalance requires a thorough evaluation to determine the underlying cause. The diagnostic process typically involves a combination of methods, including:
Physical Examination
Your doctor will perform a physical exam to assess your overall health, including your weight, blood pressure, and body mass index (BMI). They will also check for signs of hormonal imbalances, such as acne, hair loss, or changes in body shape.
Hey there, ladies! Hormonal imbalance weight gain over 40 can be a real pain in the… well, you know. But fear not! Check out the Best weight loss diet for women over 40 . It’s got all the tips and tricks to help you shed those unwanted pounds and get your hormones back in balance.
And remember, you’re not alone in this hormonal imbalance weight gain over 40 journey.
Blood Tests
Blood tests are used to measure the levels of specific hormones in your blood. These tests can help diagnose hormonal imbalances, such as thyroid disorders, pituitary disorders, and adrenal disorders.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests, such as ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans, may be used to visualize the glands that produce hormones. These tests can help identify structural abnormalities, such as tumors or cysts, that may be causing hormonal imbalances.
Other Tests
In some cases, your doctor may order other tests, such as urine analysis or genetic testing, to further evaluate your hormonal balance.
Interpretation of Test Results
The results of your tests will be interpreted by your doctor to determine if you have a hormonal imbalance. The interpretation of the results will depend on your age, sex, and overall health.
Potential Causes of Hormonal Imbalance
Hormonal imbalances can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Pituitary disorders
- Adrenal disorders
- Thyroid disorders
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
- Cushing’s syndrome
- Addison’s disease
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and treatment of hormonal imbalances is important to prevent or minimize complications. Untreated hormonal imbalances can lead to a variety of health problems, including infertility, weight gain, and heart disease.
Treatment Options for Hormonal Imbalance
When hormonal imbalance causes weight gain, it’s crucial to address the underlying hormonal disruptions. Treatment options vary depending on the specific hormone(s) affected and the individual’s overall health.
The goal of treatment is to restore hormonal balance, improve symptoms, and promote weight loss. Let’s explore some common treatment approaches:
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
HRT involves administering synthetic or bioidentical hormones to replace deficient hormones in the body. It can be used to treat imbalances caused by menopause, thyroid disorders, or other hormonal deficiencies. HRT can effectively alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being, including weight management.
Medications
Certain medications can be prescribed to regulate hormone levels or block the effects of excess hormones. For example, metformin is used to manage insulin resistance and improve blood sugar control, which can help with weight loss.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, can significantly impact hormonal balance. Eating a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help regulate blood sugar levels and reduce inflammation, which can affect hormone production. Regular exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity and supports overall hormonal health.
Supplements
Some supplements, such as herbal remedies or vitamins, may support hormonal balance. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any supplements to ensure they are safe and effective for your individual needs.
Nutritional Recommendations for Hormonal Imbalance
Nutritional balance plays a crucial role in maintaining hormonal harmony. Certain foods and dietary guidelines can support hormonal balance, reduce inflammation, and promote overall well-being.
Specific Food Recommendations
- Fruits and vegetables:Rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that support hormonal balance. Focus on berries, leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables, and citrus fruits.
- Lean protein:Provides essential amino acids for hormone production. Choose lean meats, fish, poultry, beans, and lentils.
- Healthy fats:Include omega-3 fatty acids found in fish, avocados, and nuts, which reduce inflammation and support hormone function.
- Whole grains:Rich in fiber, which helps regulate blood sugar levels and prevent hormonal imbalances.
- Fermented foods:Contain probiotics that support gut health and hormone production.
Dietary Guidelines
- Eat regular meals:Avoid skipping meals to prevent blood sugar fluctuations that can disrupt hormones.
- Stay hydrated:Drink plenty of water throughout the day to support hormone transport and elimination.
- Limit processed foods:These foods are often high in unhealthy fats, sugar, and preservatives that can interfere with hormone balance.
- Reduce caffeine and alcohol:Excessive consumption can disrupt hormone levels.
- Consider supplements:If dietary intake is insufficient, consider supplements such as vitamin D, magnesium, or zinc, which play a role in hormone regulation.
Nutrient Deficiencies
Hormonal imbalances can sometimes result from nutrient deficiencies. Common deficiencies include:
- Vitamin D:Essential for calcium absorption and hormone regulation.
- Magnesium:Involved in over 300 bodily functions, including hormone production.
- Zinc:Necessary for hormone synthesis and immune function.
To address deficiencies, focus on consuming foods rich in these nutrients or consider supplementation after consulting a healthcare professional.
Meal Plan Examples
Here’s a sample meal plan that incorporates the recommended foods: Breakfast:Oatmeal with berries and nuts Lunch:Grilled salmon salad with leafy greens and quinoa Dinner:Chicken stir-fry with brown rice and broccoli Snacks:Apple with peanut butter, yogurt with fruit
Lifestyle Factors
In addition to nutrition, certain lifestyle factors can influence hormonal balance:
- Stress management:Chronic stress can disrupt hormone levels. Engage in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature.
- Adequate sleep:Sleep deprivation can affect hormone production. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Regular exercise:Exercise can help regulate hormone levels and reduce stress.
– Discuss the role of exercise in managing hormonal imbalance
Exercise plays a crucial role in managing hormonal imbalances, particularly those associated with aging. Regular physical activity can help regulate hormone levels, improve symptoms, and promote overall well-being.
Exercise Recommendations and Guidelines
Tailoring exercise recommendations to the specific type of hormonal imbalance is essential. For example, women with estrogen dominance may benefit from exercises that increase testosterone levels, while those with low progesterone levels may focus on exercises that stimulate progesterone production.
| Hormonal Imbalance | Exercise Recommendations |
|---|---|
| Estrogen dominance | Weightlifting, interval training |
| Low progesterone | Yoga, Pilates, walking |
| Testosterone deficiency | Resistance training, sprinting |
In general, the following exercise guidelines are recommended for managing hormonal imbalance:
- Intensity:Moderate to vigorous intensity, where you can talk but not sing during exercise.
- Duration:30-60 minutes most days of the week.
- Frequency:Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week.
How Exercise Regulates Hormones
Exercise can regulate hormones in several ways:
- Increases blood flow:Exercise enhances blood flow to the ovaries, testes, and other endocrine glands, facilitating hormone production.
- Reduces stress:Exercise releases endorphins, which have mood-boosting and stress-reducing effects. Stress can disrupt hormone balance, so reducing stress levels is crucial.
- Improves insulin sensitivity:Exercise improves insulin sensitivity, which helps regulate blood sugar levels and can indirectly affect hormone balance.
Tips for Incorporating Exercise
- Find an activity you enjoy, as you’re more likely to stick with it.
- Start gradually and increase intensity and duration as you progress.
- Listen to your body and rest when needed.
- Consider working with a personal trainer or healthcare professional for guidance.
Potential Risks and Precautions
While exercise is generally safe for managing hormonal imbalance, some precautions should be considered:
- Overtraining:Avoid excessive exercise, as it can lead to hormonal imbalances.
- Hypoglycemia:People with hormonal imbalances may experience low blood sugar during exercise, so it’s essential to monitor blood sugar levels and eat a balanced meal before exercising.
- Muscle soreness:Hormonal imbalances can increase muscle soreness, so it’s important to stretch before and after exercise.
Natural Remedies for Hormonal Imbalance
Natural remedies offer a gentle approach to supporting hormonal balance. They may work by mimicking the effects of hormones, stimulating hormone production, or inhibiting hormone breakdown. While some remedies may provide relief, it’s important to note that they may not be suitable for everyone and should be used with caution.
The following table provides an overview of some natural remedies commonly used for hormonal imbalance:
| Remedy Name | Mechanism of Action | Dosage and Administration | Safety and Side Effects | Contraindications | Drug Interactions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitex (Chasteberry) | Binds to dopamine receptors in the pituitary gland, regulating prolactin and luteinizing hormone (LH) levels | 150-250 mg extract daily | Generally safe; may cause nausea, headaches, or skin reactions | Pregnancy, breastfeeding, hormone-sensitive conditions | None known |
| Maca Root | Adaptogen that supports adrenal function and hormone balance | 1-2 teaspoons of powder daily | Generally safe; may cause stomach upset | None known | None known |
| Evening Primrose Oil | Provides essential fatty acids that support hormone production | 500-1,000 mg daily | Generally safe; may cause nausea or headaches | Epilepsy, bleeding disorders | May interfere with blood thinners |
| Dong Quai | Estrogen-like herb that supports blood flow and hormone balance | 2-4 grams of root daily | Generally safe; may cause uterine contractions | Pregnancy, hormone-sensitive conditions | May interact with anticoagulants |
| Shatavari | Ayurvedic herb that supports hormonal balance and reproductive health | 1-2 teaspoons of powder daily | Generally safe; may cause diarrhea | None known | None known |
It’s important to consult a qualified healthcare professional before using any natural remedies for hormonal imbalance. They can help determine the appropriate dosage and potential interactions with other medications or health conditions.
Stress Management for Hormonal Imbalance
Stress is a significant factor that can disrupt hormonal balance. When we experience stress, our bodies release hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. While these hormones are essential for our survival, chronic stress can lead to an imbalance in these hormones, which can have a negative impact on weight gain.
Stress can affect hormonal balance by:
- Increasing cortisol levels, which can lead to increased appetite and cravings for unhealthy foods.
- Reducing the production of thyroid hormones, which can slow down metabolism and make it harder to lose weight.
- Disrupting the production of sex hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone, which can lead to weight gain around the abdomen.
Stress Management Techniques
Managing stress is crucial for maintaining hormonal balance and preventing weight gain. Here are some effective stress management techniques:
- Exercise:Exercise is a great way to reduce stress and improve overall health. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Yoga and Meditation:Yoga and meditation can help calm the mind and reduce stress levels. Try practicing yoga or meditation for 10-15 minutes each day.
- Sleep:Getting enough sleep is essential for overall health, including hormonal balance. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep each night.
- Diet:Eating a healthy diet can help reduce stress and improve hormonal balance. Focus on eating whole, unprocessed foods and limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats.
- Social support:Talking to friends, family, or a therapist can help you cope with stress and improve your overall well-being.
Sleep Hygiene for Hormonal Imbalance
Sleep is crucial for maintaining hormonal balance. When you sleep, your body produces hormones that regulate metabolism, appetite, and stress levels. Lack of sleep can disrupt these hormonal processes, leading to weight gain and other health issues.
Tips for Improving Sleep Quality
To improve sleep quality and support hormonal balance, consider the following tips:
- Create a regular sleep schedule:Go to bed and wake up around the same time each day, even on weekends. This helps regulate your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle.
- Make your bedroom conducive to sleep:Ensure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool. Use blackout curtains, a white noise machine, or earplugs to minimize distractions.
- Avoid caffeine and alcohol before bed:These substances can interfere with sleep and disrupt hormonal balance.
- Get regular exercise:Exercise can improve sleep quality, but avoid working out too close to bedtime as it can make it harder to fall asleep.
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine:Engage in calming activities before bed, such as reading, taking a warm bath, or listening to soothing music.
- See a doctor if you have trouble sleeping:If you consistently have trouble sleeping, consult a doctor to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
Complementary Therapies for Hormonal Imbalance
Complementary therapies can offer gentle support alongside medical treatment for hormonal imbalance. These therapies aim to restore balance, reduce symptoms, and promote overall well-being.
Hormonal imbalances after 40 can make weight loss a real struggle. But don’t give up hope! Check out this Meal plan for weight loss over 40 designed specifically for our changing bodies. It’s packed with tips, tricks, and delicious recipes that will help you lose weight and feel your best.
Hormonal imbalances can make weight loss challenging, but it’s not impossible. With the right plan and support, you can reach your goals.
Some complementary therapies that may be beneficial include:
Acupuncture
- Acupuncture involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body.
- It is believed to stimulate the body’s natural healing response and promote hormonal balance.
Herbal Remedies
- Certain herbs, such as chasteberry, black cohosh, and red clover, have been traditionally used to support hormonal health.
- They may help regulate menstrual cycles, reduce hot flashes, and improve mood.
Yoga and Meditation
- Yoga and meditation practices can help reduce stress, which can contribute to hormonal imbalances.
- They promote relaxation, improve sleep, and support overall well-being.
Massage Therapy
- Massage therapy can help reduce stress and improve circulation.
- It may also help relieve symptoms such as muscle tension, headaches, and fatigue.
Case Studies of Hormonal Imbalance and Weight Gain
Hormonal imbalance can lead to a myriad of health issues, including weight gain. Here are a few case studies that illustrate the impact of hormonal imbalance on weight gain and the approaches taken to address it.
Case Study 1:
Sarah’s Story
Sarah, a 45-year-old woman, had been struggling with unexplained weight gain for the past few years. She had always been active and maintained a healthy diet, but despite her efforts, the weight kept piling on. After consulting with her doctor, Sarah was diagnosed with hypothyroidism, a condition where the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone.
Over 40, hormonal imbalance can make shedding those extra pounds a real battle. If you’ve tried diet and exercise with no luck, consider Weight loss surgery after 40 . This procedure can help reset your hormones and give you the jumpstart you need to reach your weight loss goals.
Of course, hormonal imbalance weight gain over 40 is a complex issue, so it’s important to talk to your doctor about all of your options before making a decision.
Thyroid hormone plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, and its deficiency can lead to weight gain, fatigue, and other symptoms.
Sarah was prescribed thyroid hormone replacement therapy, which helped regulate her thyroid levels and gradually led to weight loss. She also made some lifestyle changes, such as increasing her physical activity and reducing stress, which further supported her weight management efforts.
Case Study 2:
John’s Story
John, a 50-year-old man, had been experiencing weight gain, decreased energy levels, and difficulty sleeping. His doctor suspected a hormonal imbalance and ordered blood tests, which revealed low testosterone levels. Testosterone is a hormone that plays a vital role in muscle mass, energy levels, and overall well-being.
John was prescribed testosterone replacement therapy, which helped improve his energy levels, mood, and sleep quality. He also incorporated regular exercise into his routine and focused on consuming a balanced diet. Over time, John was able to lose weight and regain his overall vitality.
These case studies demonstrate the impact that hormonal imbalance can have on weight gain and the importance of seeking medical advice to address the underlying cause. With appropriate treatment and lifestyle modifications, individuals can effectively manage hormonal imbalances and achieve their weight loss goals.
Outcome Summary
Unveiling the intricate interplay between hormones, aging, and weight gain, this guide empowers individuals over 40 to take charge of their hormonal health. By embracing lifestyle modifications, exploring natural remedies, and seeking professional guidance when needed, it’s possible to restore hormonal balance, shed excess weight, and embrace a renewed sense of well-being.
Query Resolution
What are the key hormonal changes that occur in women over 40?
Estrogen and progesterone levels decline, leading to a decrease in metabolism and an increase in body fat storage.
How can lifestyle factors influence hormonal imbalance?
Stress, lack of sleep, and poor diet can disrupt hormone production and contribute to weight gain.
What natural remedies can support hormonal balance?
Chasteberry, maca root, and evening primrose oil have been traditionally used to alleviate hormonal imbalances.
When should I seek professional help for hormonal imbalance?
If lifestyle changes and natural remedies do not improve symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and treatment.