Hormonal weight gain in perimenopause – As you enter the enigmatic realm of perimenopause, a cascade of hormonal shifts can wreak havoc on your weight, leaving you feeling bewildered and frustrated. But fear not, for this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and strategies to tame the hormonal weight gain beast and reclaim your body confidence.
Delve into the intricate hormonal dance of perimenopause, unraveling the mysteries behind weight gain and arming yourself with a plan to combat it. From lifestyle adjustments to medical interventions, we’ll explore a holistic approach to managing this common challenge, empowering you to regain control of your weight and embrace this new chapter with vitality.
Hormonal Changes in Perimenopause
Perimenopause is a transitional phase that marks the end of a woman’s reproductive years. During this time, the body undergoes significant hormonal changes that can lead to a variety of symptoms, including weight gain.
The most significant hormonal changes during perimenopause involve the decline in estrogen and progesterone production. Estrogen is a hormone that helps regulate metabolism, while progesterone helps balance estrogen’s effects. As these hormones decline, the body may become more likely to store fat, particularly around the abdomen.
Estrogen and Weight Gain
Estrogen plays a key role in regulating metabolism. It helps increase the body’s ability to burn fat and maintain a healthy weight. As estrogen levels decline during perimenopause, the body may become less efficient at burning fat, leading to weight gain.
Progesterone and Weight Gain
Progesterone helps balance estrogen’s effects. It helps reduce fluid retention and bloating, which can contribute to weight gain. As progesterone levels decline during perimenopause, fluid retention and bloating may become more common, leading to further weight gain.
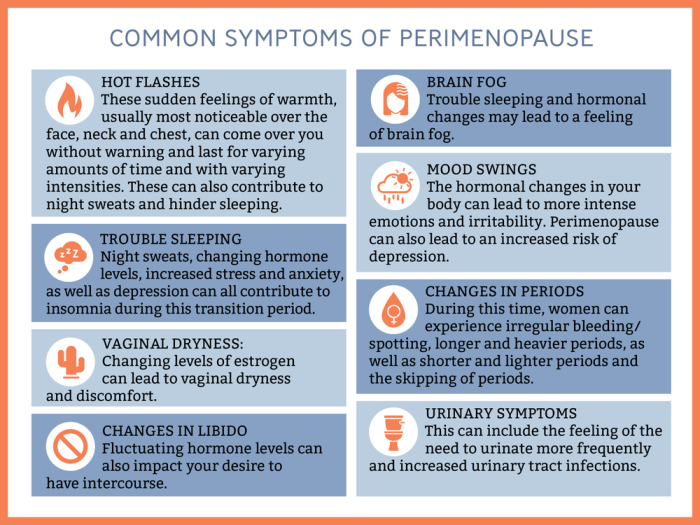
Symptoms of Hormonal Weight Gain
Weight gain during perimenopause can be a frustrating and confusing symptom. It can be difficult to know if your weight gain is due to hormonal changes or other factors, such as diet and exercise. However, there are some key symptoms that can help you differentiate between hormonal weight gain and other causes.
One of the most common symptoms of hormonal weight gain is weight gain around the middle. This is because estrogen, a hormone that helps to regulate weight, declines during perimenopause. As estrogen levels drop, the body may start to store more fat around the abdomen.
Other symptoms of hormonal weight gain include:
- Difficulty losing weight, even with diet and exercise
- Increased appetite
- Cravings for sugary or fatty foods
- Mood swings
- Hot flashes
- Night sweats
- Sleep problems
- Vaginal dryness
- Breast tenderness
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to talk to your doctor. They can help you determine if your weight gain is due to hormonal changes and recommend treatment options.
Weight Gain vs. Other Causes
There are a number of other factors that can contribute to weight gain during perimenopause, including:
- Decreased physical activity
- Poor diet
- Stress
- Medications
- Medical conditions
It is important to talk to your doctor to rule out any other potential causes of weight gain. Once other causes have been ruled out, your doctor can help you develop a treatment plan to address your hormonal weight gain.
Causes of Hormonal Weight Gain
Hormonal changes during perimenopause can lead to weight gain due to several factors:
Changes in Estrogen and Progesterone Levels
- Estrogen:Estrogen levels decline during perimenopause, affecting the body’s ability to regulate metabolism and glucose levels.
- Progesterone:Progesterone levels also decrease, which can lead to increased appetite and fluid retention.
Changes in Thyroid Hormone
Thyroid hormone levels may decrease during perimenopause, slowing down metabolism and contributing to weight gain.
Changes in Cortisol Levels
Increased cortisol levels, often associated with stress during perimenopause, can promote fat storage and weight gain.
Impact of Hormonal Weight Gain
Hormonal weight gain during perimenopause can have a significant impact on both your physical and emotional well-being.
As perimenopause sets in, hormonal shifts can trigger stubborn weight gain. But fear not, ladies! Weight loss transformations for women over 40 are possible. These inspiring stories show how women have overcome hormonal challenges to achieve their health and fitness goals.
Remember, even with hormonal hurdles, weight management is within reach.
Physically, hormonal weight gain can lead to:
- Increased body fat, especially around the abdomen
- Difficulty losing weight
- Increased risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease and diabetes
Emotionally, hormonal weight gain can lead to:
- Low self-esteem
- Negative body image
- Depression and anxiety
Managing Hormonal Weight Gain
There are a number of things you can do to manage hormonal weight gain, including:
- Diet:Eat a healthy diet that is low in calories and fat, and high in fiber. Focus on eating fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Exercise:Get regular exercise. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Lifestyle changes:Make other lifestyle changes that can help you lose weight, such as getting enough sleep, managing stress, and avoiding smoking.
Coping with the Emotional Challenges
In addition to managing the physical symptoms of hormonal weight gain, it is also important to address the emotional challenges. Here are a few tips:
- Talk to your doctor:Your doctor can help you understand the changes that are happening to your body and provide support.
- Join a support group:There are many support groups available for women who are experiencing hormonal weight gain. These groups can provide a safe and supportive environment where you can share your experiences and learn from others.
- Practice self-care:Take care of yourself both physically and emotionally. Eat healthy foods, get enough sleep, and exercise regularly. Do things that make you happy and that help you relax.
| Physical Impact | Emotional Impact | Management Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Increased body fat | Low self-esteem | Diet and exercise |
| Difficulty losing weight | Negative body image | Lifestyle changes |
| Increased risk of chronic diseases | Depression and anxiety | Coping with emotional challenges |
– Management Strategies
Managing hormonal weight gain during perimenopause involves a multifaceted approach that encompasses lifestyle changes, dietary modifications, and potential medical interventions. Implementing these strategies requires patience and consistency, but they can effectively mitigate the challenges associated with weight gain.
Lifestyle Changes
Incorporating regular physical activity into your daily routine is crucial. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. Prioritizing stress-reducing activities, such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature, can also contribute to weight management.
Hey there, ladies! Are you feeling the hormonal weight gain creep up as you approach perimenopause? Don’t worry, you’re not alone. Check out this awesome article on Weight loss before and after for women over 40 . It’s got some great tips and tricks to help you lose weight and get your body back on track.
Even though hormonal changes can make it harder to shed those extra pounds, there are still plenty of things you can do to reach your goals. So, let’s get started and kick this hormonal weight gain to the curb!
Additionally, ensuring adequate sleep duration and quality is essential for overall health and weight regulation.
Dietary Modifications
To effectively manage hormonal weight gain, it is essential to reduce calorie intake while maintaining a nutrient-rich diet. Focus on consuming lean protein, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats is also crucial.
Potential Medical Interventions
In some cases, medical interventions may be necessary to address hormonal weight gain. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) can help alleviate hormonal imbalances that contribute to weight gain. Prescription weight loss medications may also be an option if lifestyle and dietary changes are not sufficient.
Non-invasive body contouring procedures can be considered to address stubborn fat deposits.
Role of Exercise
Exercise is crucial for managing hormonal weight gain during perimenopause. It helps regulate hormones, increase metabolism, and build muscle mass, which can counteract the weight-promoting effects of hormonal changes.
Hormonal weight gain during perimenopause can be a real pain in the…well, you know. If you’re over 40 and struggling to lose weight, you may want to consider Weight loss surgery after 40 . It can be a safe and effective way to lose weight and improve your health.
But remember, hormonal weight gain during perimenopause is still a thing, so it’s important to talk to your doctor about the best way to manage it.
Specific types of exercise that are beneficial include:
Cardiovascular Exercise
- Aerobic activities like brisk walking, running, swimming, or cycling help burn calories and improve cardiovascular health.
Strength Training
- Exercises like weightlifting or resistance band training help build muscle mass, which boosts metabolism and aids in fat loss.
Flexibility Exercises
- Activities like yoga or Pilates can improve posture, reduce stress, and enhance overall well-being, contributing to weight management.
Dietary Modifications
Dietary modifications can play a crucial role in managing hormonal weight gain during perimenopause. As women over 40 experience hormonal changes, their bodies may become more resistant to insulin, leading to increased fat storage. By adopting a balanced and nutritious diet, women can support their hormonal health and mitigate weight gain.
The key dietary recommendations for managing hormonal weight gain in perimenopause include:
- Reduce processed foods, sugary drinks, and red meat.These foods contribute to inflammation, insulin resistance, and weight gain.
- Increase fruits, vegetables, and lean protein.These foods provide essential nutrients, fiber, and antioxidants that support hormonal balance and weight management.
- Choose low-fat or non-fat dairy products.Full-fat dairy products can be high in saturated fat, which can contribute to weight gain.
- Opt for whole grains over refined grains.Whole grains are a good source of fiber, which helps regulate blood sugar levels and promotes satiety.
- Limit saturated and trans fats.These unhealthy fats can raise cholesterol levels and increase the risk of weight gain.
- Replace sugary drinks with water or unsweetened tea.Sugary drinks are high in calories and can contribute to weight gain.
Sample Meal Plan
Here is a sample meal plan that incorporates the dietary recommendations for managing hormonal weight gain in perimenopause:
- Breakfast:Oatmeal with berries and nuts, or a smoothie made with fruits, vegetables, and lean protein powder
- Lunch:Salad with grilled chicken, quinoa, and vegetables, or a sandwich on whole-wheat bread with lean protein and vegetables
- Dinner:Grilled salmon with roasted vegetables and brown rice, or a vegetarian stir-fry with tofu and vegetables
- Snacks:Fruits, vegetables, nuts, or yogurt
Rationale for Dietary Recommendations
The dietary recommendations for managing hormonal weight gain in perimenopause are based on the following principles:
- Reducing inflammation:Processed foods, sugary drinks, and red meat can contribute to inflammation, which is linked to weight gain and other health problems.
- Improving insulin sensitivity:Fruits, vegetables, and lean protein can help improve insulin sensitivity, which is important for regulating blood sugar levels and preventing weight gain.
- Promoting satiety:Fiber-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, help promote satiety and reduce hunger cues.
- Supporting hormonal balance:Certain nutrients, such as those found in fruits, vegetables, and lean protein, can support hormonal balance and reduce the risk of weight gain.
By following these dietary recommendations, women over 40 can manage hormonal weight gain, improve their overall health, and feel their best during perimenopause.
Medical Interventions
Medical interventions may be considered for managing hormonal weight gain in perimenopause when lifestyle modifications alone are not sufficient.
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT), Hormonal weight gain in perimenopause
HRT involves taking synthetic hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone, to replace the declining levels of these hormones during perimenopause.
- Benefits:HRT can help reduce hot flashes, night sweats, and other menopausal symptoms. It may also help preserve bone density and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Risks:HRT can increase the risk of blood clots, stroke, and breast cancer in some women. It is important to discuss the risks and benefits with a healthcare provider before starting HRT.
Medications that Block or Inhibit Hormone Production
These medications work by blocking or inhibiting the production of hormones that contribute to weight gain, such as estrogen and testosterone.
- Benefits:These medications can be effective in reducing weight gain and improving insulin sensitivity.
- Risks:Potential side effects include hot flashes, mood changes, and irregular menstrual cycles.
Weight Loss Surgery
Weight loss surgery may be an option for women who have severe obesity and have not been able to lose weight through other methods.
- Benefits:Weight loss surgery can lead to significant weight loss and improvements in health conditions such as diabetes and heart disease.
- Risks:Weight loss surgery is a major surgery with potential risks, including infection, bleeding, and blood clots.
Lifestyle Modifications in Conjunction with Medical Interventions
Lifestyle modifications, such as diet, exercise, and stress management, are an important part of managing hormonal weight gain, regardless of whether medical interventions are used.
- Diet:A healthy diet that is low in calories and processed foods can help reduce weight gain.
- Exercise:Regular exercise can help burn calories and build muscle, which can boost metabolism and aid in weight loss.
- Stress management:Stress can contribute to weight gain by increasing levels of the stress hormone cortisol. Stress management techniques can help reduce cortisol levels and promote weight loss.
The best approach to managing hormonal weight gain will vary depending on the individual woman’s needs and circumstances. It is important to work with a healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan that includes a combination of medical interventions and lifestyle modifications.
Emotional Support
Perimenopause can be an emotionally challenging time, and the added stress of hormonal weight gain can make it even more difficult. It’s important to remember that you’re not alone, and there are people who can help you cope.
Finding Support
Talk to your doctor, a therapist, or a trusted friend or family member about what you’re going through. They can provide support and guidance, and help you develop coping mechanisms.
Long-Term Effects
Hormonal weight gain during perimenopause can have lasting consequences that extend beyond the immediate menopausal transition.
Excessive weight gain increases the risk of developing chronic health conditions, including:
Cardiovascular Disease
- Obesity raises blood pressure and cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and heart failure.
Type 2 Diabetes
- Excess weight impairs insulin sensitivity, leading to increased blood sugar levels and potentially developing type 2 diabetes.
Osteoarthritis
- Extra weight puts stress on joints, especially the knees and hips, contributing to the development of osteoarthritis.
Certain Cancers
- Obesity has been linked to an increased risk of certain types of cancer, including breast, endometrial, and colon cancer.
Sleep Apnea
- Excess weight can obstruct breathing during sleep, leading to sleep apnea, a condition characterized by frequent pauses in breathing.
Prevention Strategies
Hormonal weight gain during perimenopause can be prevented or minimized by adopting healthy lifestyle changes and dietary modifications. Here are some effective strategies:
Lifestyle Changes
- Regular Exercise:Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week. Exercise helps burn calories, boost metabolism, and reduce stress levels. (Source: CDC )
- Stress Management:Chronic stress can lead to hormonal imbalances and increased appetite. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises. (Source: NCBI )
- Adequate Sleep:Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. Sleep deprivation can disrupt hormone production and increase cravings. (Source: NCBI )
Dietary Modifications
- Nutrient-Rich Foods:Focus on consuming whole, unprocessed foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains. These foods provide essential nutrients that support hormonal balance and satiety. (Source: Harvard Health Publishing )
- Portion Control:Pay attention to portion sizes and avoid overeating. Use smaller plates and measure out food to prevent excessive calorie intake. (Source: NIDDK )
- Mindful Eating:Practice mindful eating by paying attention to hunger cues, eating slowly, and savoring each bite. This helps prevent mindless eating and overconsumption. (Source: NCBI )
Case Studies
Numerous women have successfully managed hormonal weight gain during perimenopause, employing various strategies. Here are a few case studies that highlight their approaches and provide valuable insights:
Case Study 1
- Age:47
- Diet:Reduced processed foods, increased whole grains, fruits, and vegetables
- Exercise:Regular brisk walking and yoga
- Supplements:Omega-3 fatty acids, green tea extract
- Results:Lost 15 pounds in 6 months, improved sleep, and reduced hot flashes
Case Study 2
- Age:50
- Diet:Mediterranean-style diet, emphasizing fish, lean protein, and olive oil
- Exercise:Resistance training 3 times per week, cardio 4 times per week
- Medications:Hormone replacement therapy (HRT)
- Results:Maintained weight, improved muscle mass, and reduced joint pain
Case Study 3
- Age:48
- Diet:Plant-based diet, avoiding processed foods and animal products
- Exercise:Daily meditation and mindfulness practices
- Supplements:Ashwagandha, adaptogenic herbs
- Results:Reduced stress and anxiety, improved mood, and lost 10 pounds in 4 months
These case studies demonstrate that hormonal weight gain during perimenopause can be effectively managed through a combination of dietary modifications, exercise, and emotional support. The specific strategies may vary depending on individual needs and preferences, but the key principles remain consistent.
Limitations and Applicability
While these case studies provide valuable insights, they have limitations. The sample size is small, and the findings may not be generalizable to all women. Additionally, the results may be influenced by factors such as genetics, overall health, and socioeconomic status.
However, the strategies employed in these cases can serve as a starting point for women seeking to manage hormonal weight gain during perimenopause.
Frequently Asked Questions: Hormonal Weight Gain In Perimenopause
During perimenopause, women experience a range of hormonal changes that can lead to weight gain. Understanding these changes and their effects can help you manage your weight and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Hormonal Changes During Perimenopause
- Estrogen Decline:Estrogen helps regulate metabolism and fat distribution. As estrogen levels decline, the body becomes less efficient at burning calories and more likely to store fat, particularly around the abdomen.
- Progesterone Fluctuations:Progesterone helps balance estrogen and prevent fluid retention. During perimenopause, progesterone levels fluctuate, leading to bloating and weight gain.
- Increased Cortisol:Cortisol is a stress hormone that can trigger fat storage. During perimenopause, stress levels may increase due to hormonal changes and life events, leading to weight gain.
Symptoms of Hormonal Weight Gain
- Weight gain around the abdomen
- Difficulty losing weight
- Increased body fat percentage
- Bloating and fluid retention
- Changes in body shape and composition
Prevention and Reduction Strategies
Preventing or reducing hormonal weight gain during perimenopause requires a multifaceted approach, including:
- Exercise:Regular exercise helps burn calories, build muscle, and improve metabolism.
- Dietary Modifications:Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats.
- Stress Management:Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature.
- Sleep:Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Emotional Support:Surround yourself with supportive family and friends who understand your experiences.
Treatment Options
If lifestyle changes alone are not sufficient, medical interventions may be considered:
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT):HRT can help balance hormone levels and reduce weight gain.
- Prescription Weight Loss Medications:Certain medications can suppress appetite or increase metabolism.
- Surgery:In severe cases, surgery may be an option to remove excess fat or alter the digestive system.
Final Review
Remember, managing hormonal weight gain in perimenopause is a journey, not a destination. Embrace the ups and downs, seek support when needed, and celebrate your progress along the way. With determination and the strategies Artikeld in this guide, you can conquer the hormonal weight gain battle and emerge stronger, healthier, and more confident than ever before.
User Queries
What are the hormonal changes that occur during perimenopause that can lead to weight gain?
During perimenopause, declining estrogen levels disrupt metabolism, increase appetite, and promote fat storage, particularly around the abdomen.
What are the symptoms of hormonal weight gain?
Symptoms include unexplained weight gain, especially around the belly, increased body fat, and difficulty losing weight despite exercise and diet.
How can I prevent or reduce hormonal weight gain during perimenopause?
Focus on a nutrient-rich diet, engage in regular exercise, manage stress, and consider hormone replacement therapy if necessary.
What are the treatment options for hormonal weight gain during perimenopause?
Treatment options include lifestyle modifications, hormone replacement therapy, prescription weight loss medications, and non-invasive body contouring procedures.