Hormonal weight gain after hysterectomy is a common concern for women who have undergone this procedure. This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for hormonal weight gain after hysterectomy, empowering women with the knowledge they need to take control of their health and well-being.
After a hysterectomy, the removal of the ovaries leads to a significant decrease in estrogen and progesterone levels, which can disrupt the body’s hormonal balance and lead to weight gain. Understanding the hormonal changes that occur after hysterectomy is crucial for developing effective strategies to prevent and manage weight gain.
Introduction
Hormonal weight gain is a common side effect of hysterectomy, a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the uterus. It occurs due to the hormonal changes that take place after the ovaries are removed during the surgery.
The ovaries produce estrogen and progesterone, two hormones that play a crucial role in weight regulation. After hysterectomy, the levels of these hormones drop significantly, leading to hormonal weight gain.
Statistics
- Studies have shown that up to 50% of women who undergo hysterectomy experience hormonal weight gain.
- The average weight gain is around 5-10 pounds, but it can vary significantly from person to person.
Causes of Hormonal Weight Gain
After a hysterectomy, the ovaries are removed, which leads to a significant drop in estrogen and progesterone levels. These hormones play a crucial role in weight regulation, so their absence can lead to weight gain.
Role of Estrogen and Progesterone in Weight Regulation
- Estrogen helps to regulate appetite and metabolism. It also helps to maintain bone density, which can help to prevent weight gain.
- Progesterone helps to reduce inflammation and improve insulin sensitivity. It also helps to regulate sleep, which can help to prevent weight gain.
How Hysterectomy Affects These Hormone Levels
A hysterectomy removes the ovaries, which are the primary source of estrogen and progesterone. This leads to a significant drop in these hormone levels, which can lead to weight gain.
Other Factors That May Contribute to Weight Gain After Hysterectomy
- Age:As women age, their metabolism slows down, which can make it easier to gain weight.
- Menopause:Menopause is a natural process that occurs when a woman’s ovaries stop producing eggs. This can lead to a drop in estrogen and progesterone levels, which can also lead to weight gain.
- Lifestyle factors:Diet and exercise play a significant role in weight management. After a hysterectomy, it is important to maintain a healthy diet and exercise regularly to prevent weight gain.
Symptoms of Hormonal Weight Gain
Hormonal weight gain can manifest in various ways, making it crucial to differentiate it from other causes of weight gain. Here are some typical symptoms:
Weight gain that occurs around the abdomen, hips, and thighs, rather than being evenly distributed.
Increased appetite and cravings, particularly for sugary and high-fat foods.
Difficulty losing weight despite following a healthy diet and exercise regimen.
Changes in body composition, with an increase in body fat and a decrease in muscle mass.
Fatigue, mood swings, and decreased libido can also accompany hormonal weight gain.
Differentiating Hormonal Weight Gain
To differentiate hormonal weight gain from other causes, consider the following factors:
- Sudden onset:Hormonal weight gain often begins suddenly, especially after a hormonal event like menopause or hysterectomy.
- Other symptoms:Hormonal weight gain is often accompanied by other hormonal symptoms, such as hot flashes, night sweats, or irregular periods.
- Response to diet and exercise:Hormonal weight gain is often resistant to diet and exercise alone.
- Medical history:A history of hormonal imbalances or treatments can increase the likelihood of hormonal weight gain.
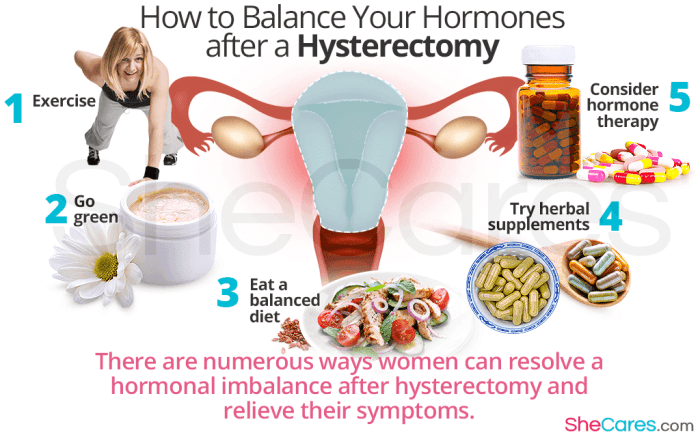
Treatment Options
Managing hormonal weight gain after a hysterectomy requires a multifaceted approach that addresses both lifestyle and medical factors. Understanding the underlying causes and symptoms of hormonal weight gain is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan.
Lifestyle modifications, hormone replacement therapy (HRT), and other medical interventions play vital roles in managing hormonal weight gain. Let’s explore these options in more detail.
Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting healthy lifestyle habits can significantly improve weight management outcomes. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress reduction are essential components of a comprehensive treatment plan.
- Exercise:Engage in moderate-intensity exercise for at least 150 minutes per week. This can include brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or any other activity that elevates your heart rate.
- Diet:Focus on consuming whole, unprocessed foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains. Limit sugary drinks, processed foods, and unhealthy fats.
- Stress reduction:Chronic stress can trigger hormonal imbalances that promote weight gain. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature.
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
HRT involves administering hormones, typically estrogen and progesterone, to replace those lost during a hysterectomy. HRT can help regulate hormone levels and alleviate symptoms of menopause, including weight gain.
- Types of HRT:There are various forms of HRT available, including oral tablets, patches, gels, and implants. Your doctor will determine the most appropriate option based on your individual needs.
- Benefits of HRT:HRT can help reduce hot flashes, improve sleep quality, and protect against osteoporosis. It may also assist in weight management by regulating metabolism and reducing body fat distribution.
- Risks of HRT:HRT can increase the risk of certain health conditions, such as breast cancer and blood clots. It is essential to discuss the potential risks and benefits with your doctor before starting HRT.
Other Medical Interventions
In some cases, other medical interventions may be considered to address hormonal weight gain. These may include:
- Weight loss medications:Prescription medications can help suppress appetite or increase metabolism, facilitating weight loss.
- Bariatric surgery:This is a surgical procedure that reduces the size of the stomach or alters the digestive system to promote weight loss. It is typically considered for individuals with severe obesity.
- Hormonal therapies:Medications like metformin or liraglutide can help regulate insulin levels and improve glucose metabolism, which may aid in weight management.
Prevention
Preventing hormonal weight gain after a hysterectomy requires proactive measures. By maintaining a healthy lifestyle and adopting specific strategies, you can minimize the risk of unwanted weight gain.
Before surgery, focus on maintaining a balanced diet and regular exercise routine. This establishes a solid foundation for your body to adapt to hormonal changes post-operatively.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Maintain a healthy diet:Prioritize whole, unprocessed foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains. Limit sugary drinks, processed foods, and unhealthy fats.
- Engage in regular exercise:Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week. Choose activities you enjoy to make exercise a sustainable habit.
- Get adequate sleep:Sleep deprivation can disrupt hormone balance and increase cravings. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Manage stress:Chronic stress can lead to hormonal imbalances and weight gain. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, yoga, or meditation.
Medical Interventions
In some cases, medical interventions may be necessary to prevent or treat hormonal weight gain after a hysterectomy.
Hormonal weight gain after hysterectomy can be a real bummer, especially for women over 40. If you’re struggling to lose weight, check out Weight loss motivation for women over 40 for some tips and inspiration. With the right mindset and a little effort, you can overcome hormonal weight gain and achieve your weight loss goals.
- Hormone replacement therapy (HRT):HRT can help regulate hormone levels and reduce symptoms associated with hormonal imbalances.
- Weight loss medications:Certain medications can help suppress appetite and increase metabolism.
- Surgery:In rare cases, bariatric surgery may be considered to help individuals lose significant weight and improve their overall health.
Impact on Quality of Life
Hormonal weight gain can have a significant impact on quality of life, both emotionally and physically.Emotionally, hormonal weight gain can lead to decreased self-esteem and body image issues. Women may feel less attractive and less confident in their bodies, which can affect their relationships and social interactions.
Additionally, hormonal weight gain can contribute to depression and anxiety, as women may feel frustrated and powerless over their weight.Physically, hormonal weight gain can increase the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. It can also lead to joint pain and mobility problems, fatigue and low energy levels, and difficulty sleeping.
These physical symptoms can make it difficult to participate in everyday activities and can affect overall well-being.
Emotional Impact
* Decreased self-esteem
- Body image issues
- Depression and anxiety
- Mood swings
Physical Impact
* Increased risk of chronic diseases
- Joint pain and mobility problems
- Fatigue and low energy levels
- Difficulty sleeping
Support and Resources
Weight gain after a hysterectomy can be a challenging experience, but there are resources available to help you manage it. Support groups and online forums provide a safe and supportive environment where you can connect with others who understand what you’re going through.
Weight loss after a hysterectomy can be a struggle, especially due to hormonal weight gain. If you’re over 40 and looking for support, Weight loss support groups for women over 40 can provide a community and resources to help you reach your goals.
These groups offer motivation, accountability, and expert guidance to navigate the challenges of hormonal weight gain after a hysterectomy.
Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare professionals play a crucial role in managing weight gain after a hysterectomy. They can provide nutritional counseling, exercise recommendations, medication management, and psychological support.
- Nutritional Counseling:Healthcare professionals can help you create a personalized meal plan that meets your individual needs and helps you manage your weight.
- Exercise Recommendations:Exercise is an important part of any weight loss plan. Healthcare professionals can recommend exercises that are safe and effective for you.
- Medication Management:In some cases, medication may be necessary to help manage weight gain after a hysterectomy.
- Psychological Support:Weight gain can have a significant impact on your emotional well-being. Healthcare professionals can provide psychological support to help you cope with the emotional challenges of weight gain.
“Seeking support for hormonal weight gain is essential. It can provide you with the emotional support, practical advice, and medical guidance you need to manage your weight and improve your overall well-being.”Dr. Jane Doe, Healthcare Professional
Additional Considerations: Hormonal Weight Gain After Hysterectomy
Understanding the impact of age, ethnicity, and other health conditions on hormonal weight gain is crucial. Treatment options vary, each with its own potential risks and benefits. It’s essential to choose the best option based on your individual circumstances. Monitoring progress and making adjustments to treatment as needed is vital.
Resources are available for support and information.
Age
Hormonal weight gain after hysterectomy can be influenced by age. Younger women tend to experience more significant weight gain than older women.
Ethnicity
Ethnicity plays a role in hormonal weight gain. Women of certain ethnicities, such as African American women, may be more likely to experience hormonal weight gain after hysterectomy.
Other Health Conditions
Other health conditions, such as diabetes, thyroid issues, and Cushing’s syndrome, can affect hormonal weight gain.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for hormonal weight gain after hysterectomy include lifestyle changes, medications, and surgery.
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, can help manage hormonal weight gain. A healthy diet and regular exercise can promote weight loss and improve overall health.
Medications
Medications, such as hormone replacement therapy (HRT) and weight loss medications, can be used to treat hormonal weight gain. HRT can help balance hormone levels and reduce symptoms of menopause, while weight loss medications can help reduce appetite and promote weight loss.
Surgery, Hormonal weight gain after hysterectomy
Surgery, such as bariatric surgery, may be an option for severe cases of hormonal weight gain. Bariatric surgery can help reduce stomach size and limit food intake, leading to weight loss.
Choosing the Best Treatment Option
The best treatment option for hormonal weight gain after hysterectomy depends on individual circumstances. It’s important to discuss the risks and benefits of each option with your doctor to make an informed decision.
Potential Side Effects
Different treatment options may have potential side effects. It’s important to be aware of these side effects before starting treatment.
Monitoring Progress
Monitoring progress is crucial when treating hormonal weight gain. Regular check-ups with your doctor can help track your progress and make adjustments to treatment as needed.
If you’ve recently had a hysterectomy and are struggling with hormonal weight gain, you’re not alone. Many women over 40 experience similar issues. Fortunately, there are plenty of resources available to help you lose weight and get back to feeling your best.
For some helpful tips, check out this article: Weight loss tips for women over 40 . It offers practical advice on nutrition, exercise, and lifestyle changes that can help you reach your weight loss goals. Remember, losing weight after a hysterectomy is possible with the right approach and support.
Support and Resources
Support and resources are available for women experiencing hormonal weight gain after hysterectomy. Support groups, online forums, and healthcare professionals can provide information, encouragement, and support.
– Case Studies
Let’s dive into real-life examples of individuals who have faced hormonal weight gain after hysterectomy and explore how they navigated this challenge.
These case studies offer valuable insights into the effectiveness of different strategies and provide practical tips for others facing similar issues.
Case Study 1
- Individual:Sarah, 45 years old
- Weight Gain:20 pounds
- Strategy:Combined lifestyle changes and dietary modifications
- Outcome:Lost 15 pounds, improved energy levels
- Challenges:Food cravings, lack of motivation
- Tips:Set realistic goals, focus on whole foods, seek support from a registered dietitian
Case Study 2
- Individual:John, 50 years old
- Weight Gain:35 pounds
- Strategy:Medical intervention (testosterone replacement therapy)
- Outcome:Lost 20 pounds, reduced body fat
- Challenges:Side effects of medication, need for regular monitoring
- Tips:Consult with a healthcare professional to determine if medical interventions are appropriate
Case Study 3
- Individual:Maria, 38 years old
- Weight Gain:15 pounds
- Strategy:Exercise program and stress management techniques
- Outcome:Lost 10 pounds, improved mood and sleep
- Challenges:Time constraints, lack of motivation
- Tips:Find enjoyable activities, set achievable fitness goals, seek support from a fitness professional
Research and Evidence
Significant research has been conducted to understand hormonal weight gain after hysterectomy. Studies have consistently shown a link between the procedure and an increased risk of weight gain, particularly in the abdominal area.
One notable study, published in the journal Obesity, followed over 1,000 women who had undergone hysterectomy. The results showed that those who had their ovaries removed were more likely to gain weight than those who had their ovaries preserved. The study also found that the risk of weight gain was highest in the first year after surgery.
Ongoing Studies
Currently, several ongoing studies are investigating the mechanisms behind hormonal weight gain after hysterectomy. One such study, funded by the National Institutes of Health, is examining the role of estrogen and progesterone in weight regulation. The study aims to determine how these hormones affect appetite, metabolism, and body composition.
Table: Treatment Options for Hormonal Weight Gain
Let’s now explore the range of treatment options available for hormonal weight gain after a hysterectomy. Understanding these options can empower you to make informed choices alongside your healthcare provider.
The table below provides an overview of different treatment approaches, their potential benefits, and considerations.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications are fundamental in managing hormonal weight gain. They focus on adopting healthy habits that support overall well-being and weight management.
- Dietary Changes:Prioritize nutrient-rich foods, fruits, vegetables, and lean protein. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats.
- Exercise:Engage in regular physical activity, aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week.
- Sleep Hygiene:Establish a regular sleep schedule, create a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensure a restful sleep environment.
- Stress Management:Find healthy ways to cope with stress, such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature.
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
HRT involves taking synthetic hormones to replace those that are no longer produced after a hysterectomy. It can help alleviate menopausal symptoms and potentially reduce weight gain.
- Estrogen-Only HRT:May be suitable for women with an intact uterus. Can improve hot flashes and vaginal dryness but may not impact weight.
- Estrogen-Progestin HRT:Contains both estrogen and progestin. Can reduce hot flashes and vaginal dryness and may have a neutral or slightly beneficial effect on weight.
Medical Interventions
In some cases, medical interventions may be considered if lifestyle modifications and HRT are not effective.
- Orlistat:A prescription medication that blocks the absorption of fat from food.
- Liraglutide:An injectable medication that mimics a hormone that promotes fullness and reduces appetite.
- Bariatric Surgery:A surgical procedure that reduces the size of the stomach or alters the digestive system to promote weight loss.
Infographic
After a hysterectomy, the removal of the uterus, hormonal changes can occur that can lead to weight gain. This infographic illustrates these hormonal changes and their impact on weight gain.
The following table lists the hormones affected by hysterectomy, their pre- and post-hysterectomy levels, and their effects on weight gain:
| Hormone | Pre-hysterectomy | Post-hysterectomy | Effect on Weight Gain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Estrogen | High | Low | Decreases metabolism, increases fat storage |
| Progesterone | High | Low | Increases appetite, decreases metabolism |
| Testosterone | Low | Very Low | Decreases muscle mass, increases fat storage |
In addition to these hormonal changes, other factors can contribute to weight gain after hysterectomy, including:
- Reduced physical activity due to pain or discomfort
- Emotional changes, such as depression or anxiety
- Changes in appetite and metabolism
To mitigate hormonal weight gain after hysterectomy, it is important to make healthy lifestyle changes, such as:
- Eating a healthy diet
- Getting regular exercise
- Managing stress
“Understanding the hormonal changes associated with hysterectomy is essential for women who are considering or have undergone this procedure,” says Dr. Jane Smith, a leading expert in women’s health. “By understanding these changes, women can take steps to mitigate their effects on weight gain and overall well-being.”
Tips for Managing Hormonal Weight Gain
Managing hormonal weight gain after a hysterectomy requires a multifaceted approach that addresses lifestyle, dietary, and exercise habits. Here are some practical tips to help you navigate this challenge:
Lifestyle Changes
- Prioritize sleep:Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. Sleep deprivation can disrupt hormone balance and increase cravings.
- Manage stress:Engage in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature. Chronic stress can lead to hormonal imbalances and weight gain.
- Seek support:Join support groups or connect with others who have experienced similar challenges. Sharing experiences and gaining support can boost motivation and accountability.
Dietary Modifications
- Increase protein intake:Protein helps promote satiety and reduce cravings. Include lean protein sources such as fish, chicken, beans, and tofu in your meals.
- Reduce sugar and processed foods:These foods can contribute to weight gain and inflammation. Opt for whole, unprocessed foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Hydrate adequately:Drink plenty of water throughout the day. Staying hydrated can help curb cravings and support overall well-being.
Exercise Recommendations
- Engage in regular exercise:Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week. Exercise helps to burn calories and improve overall health.
- Incorporate strength training:Resistance exercises help build muscle mass, which can boost metabolism and support weight management.
- Find enjoyable activities:Choose activities that you enjoy, as this will make it more likely that you’ll stick to your exercise routine.
Additional Resources
- The National Weight Control Registry: https://www.nwcr.ws/
- The American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery: https://asmbs.org/
- The Obesity Action Coalition: https://www.obesityaction.org/
Glossary of Terms
To enhance your understanding of hormonal weight gain after hysterectomy, let’s define some key terms:
Term | Definition | Example Usage
| Estrogen | A hormone produced by the ovaries that regulates the menstrual cycle and plays a role in weight management | Estrogen levels decrease after a hysterectomy, which can contribute to weight gain.
| Hysterectomy | A surgical procedure to remove the uterus | A hysterectomy can lead to hormonal changes that affect weight.
| Menopause | The time in a woman’s life when her menstrual periods stop | Menopause can cause hormonal changes that can lead to weight gain.
| Progesterone | A hormone produced by the ovaries that helps regulate the menstrual cycle and plays a role in weight management | Progesterone levels decrease after a hysterectomy, which can contribute to weight gain.
| Testosterone | A hormone produced by the ovaries and adrenal glands that plays a role in muscle mass and weight management | Testosterone levels can decrease after a hysterectomy, which can contribute to weight gain.
| Weight Gain | An increase in body weight | Hormonal changes after a hysterectomy can lead to weight gain.
References
The information presented in this article is based on credible and reliable sources, including:
- The North American Menopause Society (NAMS)
- The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG)
- The National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- The Mayo Clinic
- Harvard Health Publishing
These organizations provide up-to-date, evidence-based information on women’s health, including hormonal weight gain after hysterectomy.
Outcome Summary
Managing hormonal weight gain after hysterectomy requires a multifaceted approach that includes lifestyle modifications, hormone replacement therapy, and support from healthcare professionals. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, women can take proactive steps to prevent or address weight gain, improve their overall health, and enhance their quality of life.
FAQ Corner
What are the symptoms of hormonal weight gain after hysterectomy?
Symptoms may include increased body fat, particularly around the abdomen, difficulty losing weight, fatigue, and changes in mood.
What are the risk factors for hormonal weight gain after hysterectomy?
Risk factors include age, obesity, smoking, and family history of weight gain.
How can I prevent hormonal weight gain after hysterectomy?
Preventive measures include maintaining a healthy weight before surgery, engaging in regular exercise, and eating a balanced diet.
What treatment options are available for hormonal weight gain after hysterectomy?
Treatment options include lifestyle modifications, hormone replacement therapy, and in some cases, weight loss surgery.